In 2008 a wave of murders of albinos in eastern and central Africa attracted worldwide attention and condemnation even though it wasn’t the first time albinos were targeted in countries like Tanzania, Burundi and Malawi.
In June 2008, a New York Times online edition aired a news brief on albino killings in Tanzania, which caused a sensation. In July 2008, a BBC journalist, Vicky Ntetema, posed as a businesswoman who wanted to get rich quick and consulted 10 witchdoctors in Tanzania. Several witchdoctors promised to get her a magic concoction mixed with ground albino organs. The starting price was $2,000 for the vital organs. Later she had to go in hiding after receiving death threats because of her undercover work. A BBC video on the horrifying spate of killings of albinos in Tanzania, broadcast in August of the same year, was later taken off the air. Also in July Al Jazeera presented a video on the fate of albinos in Tanzania (Part 1 and Part 2). The European Union condemned the ritual murdering of albinos (September, 2008), followed by UNICEF (December, 2008). By then, according to the Tanzania Albino Society (TAS), more than 35 albinos had been killed in 2008 alone, with many other such cases unreported. For more cases, covering the 2003 – 2010 period, you’re welcome to visit my archives. Unfortunately, many links have expired. (For this reason I copy all articles and publish them on the present site while acknowledging their origin).
It’s important to mention that ‘Under The Same Sun’ founder Peter Ash estimates the total number of deadly victims to be twice the official figure in a December 3, 2008 interview. Viewers are warned that the interview can be shocking because of the graphic nature of the story.
The NGO Under The Same Sun helps people with albinism overcome often deadly discrimination through education and advocacy. UTSS was started by Peter Ash, a former pastor and Canadian businessman with albinism, and Vicky Ntetema, mentioned earlier, Tanzania’s BBC bureau chief whose report in July 2008 broke the story to the world of the gruesome murders of persons with albinism in Tanzania. UTSS was founded in 2008. Visit the impressive site of Under The Same Sun, a comprehensive site about Persons with Albinism in Tanzania.

Under The Same Sun helps people with albinism overcome often deadly discrimination through education and advocacy
The following article dates from 2015 but as forthcoming posts will also demonstrate, the fight against discrimination of people with albinism is far from over, and therefor I want to congratulate Under The Same Sun, the Tanzania Albinism Society, and other organizations supporting the same cause for their valuable work and wish them success in the future. May their work soon be no longer needed! (webmaster FVDK)
Published on May 13, 2015
By Daniel Wesangula
The Guardian

Around 30,000 people with albinism are thought to be living in Tanzania. Photograph: Ana Palacios
Albinos live with the risk of being killed, their body parts fetching high prices for witchcraft – but NGOs hope that change is coming.
“This is possibly the worst time to be a person living with albinism in Tanzania,” says Amir Manento.
In October, citizens will go to the polls to vote in presidential and parliamentary elections. “Every election period brings with it a new cycle of killings. In between we have other smaller elections translating to more abductions, more killings.” Manento, a retired judge and human rights activist, has been at the forefront of campaigning for the rights of people living with albinism for decades. “We see an increase of witchcraft and the use of human body parts, particularly albino body parts, in the run-up to the general elections.” Albino body parts are associated with good luck, and as the country gears up for the elections, the demand for good luck charms goes up. Sacrifices during this time are thought by some to be a sure way of guaranteeing victory in the polls.
“Albino hunting came into the limelight around 10 years ago, particularly within the fishing and mining communities,” says Dr Benson Bana, a political science and public administration lecturer at the University of Dar es Salaam. Bana believes that some of the roots of the problem lie in the financial downturn in the area around Lake Victoria, one of the regions where there have been the most killings and abductions.
“A certain poverty touched our people after the privatisation of fishing activities in Lake Victoria,” says Bana. “Everything was being controlled, from where one could fish to the size of the holes in his fishing net. The result was diminished harvests. Every above-average catch by the little guys was then attributed to superstition. This is when witchdoctors started peddling the belief that people living with albinism or their body parts, most of whom coincidentally live in these regions, could be used as good luck charms.”
Bana believes that this devastating association was then passed on to neighbouring mining communities. “Eventually it caught wind and was looked upon as a legitimate way of acquiring riches and power by some individuals. Hence the association with politicians.”
Tanzania is thought to have one of the world’s largest populations of people living with albinism, a congenital disorder that robs skin, eyes and hair of their pigment. But for years this population of about 30,000 people has existed under the threat of abductions and ritual killings, and in recent years the situation appears to have worsened.
According to a report by the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, a complete set of Albino body parts – including all four limbs, genitals, ears, tongue and nose – can fetch up to $75,000 (pdf).
The Tanzania Albinism Society says it is almost impossible to know the numbers of those abducted or killed since the beginning of the year. What they are sure of, though, is that the number of victims will be higher than the two cases that made it into police records in 2013.
“Even last year the numbers might have been higher because these crimes are very intimate. Mostly a close family member, even a father, is involved in the killings and abductions. In such cases silence wins; his wife will probably be an accomplice in the crime. Nothing will be said of the matter again and the police will have no chance of prosecuting anyone,” says Severin Edward, programme coordinator for the Tanzanian Albinism Society.
A total of 155 cases of violation of albino rights have been reported to Tanzanian authorities since 2009, according to a study (pdf) released in March by Under The Same Sun, an NGO working to combat discrimination against people with albinism.
“Of these cases, 75 were deaths. We have also received 18 reports of grave violations,” said Don Sawatzky, director of operations for UTSS. The study, which gathered together data from 25 different countries in Africa, found reports of 145 albino killings, in addition to 226 violations that include mutilations, other forms of violence, and kidnappings.
UTSS has been actively pushing the United Nations for four key resolutions aimed at ending all forms of discrimination of people living with albinism.
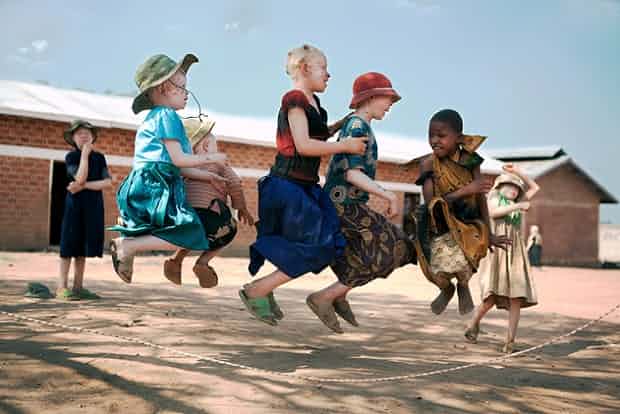

A total of 155 cases of violation of albino rights have been reported to Tanzanian authorities since 2009.
Photograph: Ana Palacios
However, Sawatzky argues that to describe the killings as a phenomenon propelled by recent economic hardship would be “to accept the easy answer”.
“Nobody really knows the origin of the killings, since documentation in Africa is not common other than through oral tradition. All we know for sure is that albinism has been ‘mythologised’ since time beyond memory. Muti murders, or ‘medicine’ killings, have a deep, longstanding history, and are a familiar concept to most Africans,” he says. In Kenya’s capital, Nairobi, the nation’s first albino member of parliament, Isaac Mwaura, says it is time measures are put in place to end these killings and abductions, and that existing laws need to be adhered to by all affected countries.
“Kenya has strict trafficking laws, the same as Tanzania. What makes it possible for criminals to take our children, mothers, fathers or brothers across borders and sell them off like commodities to witch doctors? Enforcement of laws is one of the weakest links in this war. We have become the hunted. Neither we nor our children are safe. Fathers are betraying their children’s trust and selling them off like unwanted baggage. Mothers are conspiring to traffic their own flesh and blood to senseless deaths.”
In Tanzania the government has been working with NGOs and civil society, and results are now being seen. “Never before have we seen so much effort from the government and the general public. At least we are now getting convictions, primarily because investigations are more thorough and new laws are being set up,” says Manento. “Although no executions have taken place, a total of 17 individuals have received the death sentence, some of them as recently as March, when four individuals, including the husband of the murdered victim, were convicted,” he said.
To win this war, NGOs at the forefront believe collusion within the community must come to an end. “We must educate families to understand that having such a child is not a gateway to quick riches. We then encourage the rest of the community to speak up,” says Edward. “The society needs to be more empowered and supported to co-operate. For instance, when family members are involved in killings or abductions it is quite difficult to get witnesses, because even they are not assured of their security.”
Sawatzky also believes that the war will be won, just not in the near future. “Like all forms of discrimination, it will take several generations to achieve. I will not see the war won in my lifetime. The youth and future generations are the best answer to this war,” he said.
More community sensitisation needs to be achieved, says Justus Kamugisha, regional police chief in Shinyanga, in the north of the country. “We need to make our people understand that there are no shortcuts to prosperity. Only hard, honest work pays. Taking the life of someone else, regardless of his condition, is simply murder, for which you will be charged.”
Source: The Guardian, May 13, 2015
More:
Albinism in Tanzania: safe havens in schools and support centers – in pictures
Photographs by Ana Palacios – May 13, 2015
Tanzania bans witchdoctors in attempt to end albino killings,
The Guardian, January 14, 2015
Tanzania albino murders: ‘More than 200 witchdoctors’ arrested
BBC, March 12, 2015
Witchcraft and the law in Tanzania
The Guardian, September 26, 2008
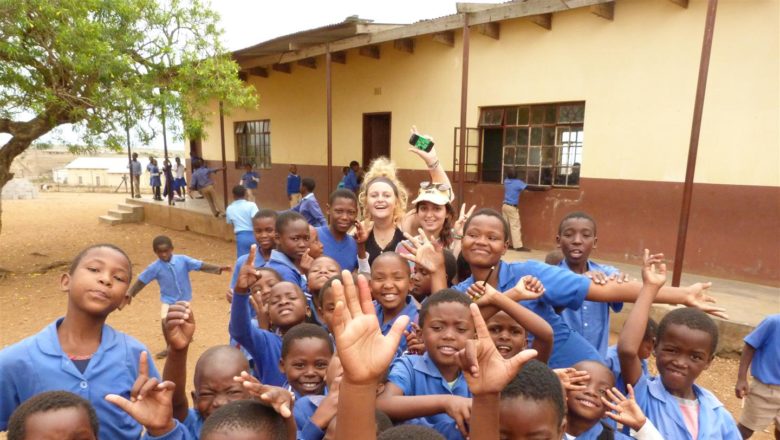
 Some 250 pupils from one community in eSwatini have abandoned school over fears linked to the recent spate of ritual kidnappings and murders.
Some 250 pupils from one community in eSwatini have abandoned school over fears linked to the recent spate of ritual kidnappings and murders.