It’s a tradition based on superstition and probably as old as humankind: to blame misfortune, an accident, bad harvest or a disease on a weaker person in society who then has to prove not being guilty of the accusation by drinking a poison. When surviving the ordeal the accused proves to be innocent. However, death confirms his or her assumed guilt.
It’s likely that this ugly practice exists all over the African continent. On previous occasions I have posted articles on ‘trial by ordeal’ in Liberia. This West African country is located 3,600 kilometers (or 2,236 miles) from Angola – as the crow flies – but the practice of trial by ordeal, locally called ‘sasswood (or sassywood) trial or ordeal’, is notorious in Africa’s oldest republic despite being banned by the government. See my posts of July and August 2020:
Liberia: Picnicess citizens say herbalist Tamba Bundo is doing well by exposing wizards, witches and ritualistic killers (August 30, 2020)
Liberia: woman dies after reportedly taking ‘sassywood’ to clear her innocence from witchcraft allegations (August 29, 2020)
Liberia: adolescent girl tortured, accused of witchcraft (July 5, 2020)
The ‘crazy’ practice – proving one is not guilty of an accusation is the opposite of the accepted rule of law when authorities have to prove a person is guilty of an alleged crime – makes victims on an unknown but unacceptable scale, not only in Liberia, but also in other African countries (as well as elsewhere on Planet Earth). In 2009 seven people, who were accused of witchcraft in Liberia – in River Gee County – died of whom two died after drinking the sasswood poison.
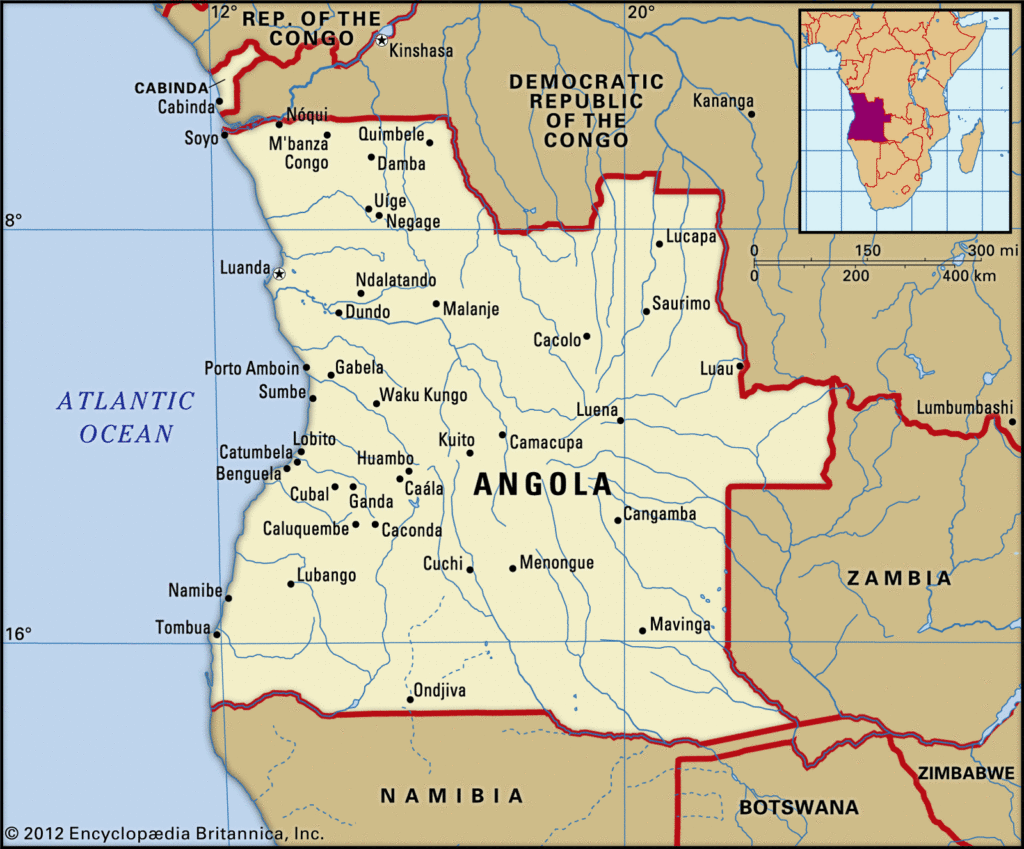
In Angola the reported deadly ‘trial by ordeall’ in Angola caused the death of more than 50 innocent people accused of being sorcerers.
These practices must be stopped!
(FVDK)

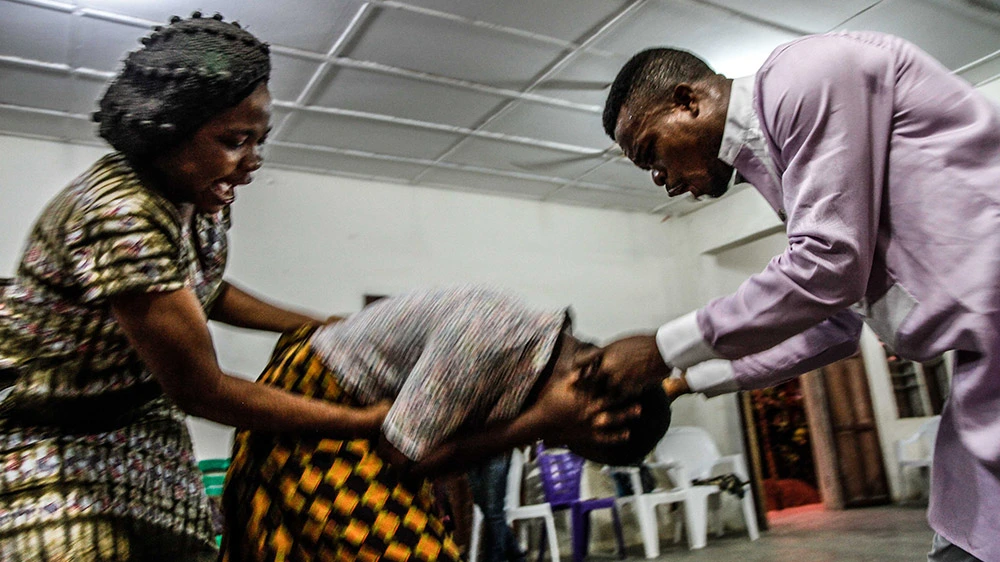
(illustration not related to the story below)
The witch-trials of Angola: Mass ritual killing as 50 are poisoned to death after being forced to drink mysterious herbal potion to prove they were not sorcerers
- Around 50 people died after being made to drink a herbal poison
- They were forced to prove they weren’t sorcerers
- Politicians accused traditional healers of making the deadly herbal drink
Published: March 14, 2024
By: Perkin Amalaraj – Daily Mail, UK
About 50 people have died in Angola after being forced to drink an herbal potion to prove they were not sorcerers, police and local officials said on Thursday.
The deaths occurred between January and February near the central town of Camacupa, according to Luzia Filemone, a local councillor.
Speaking to the national radio broadcaster, she accused traditional healers of administering the deadly concoction.
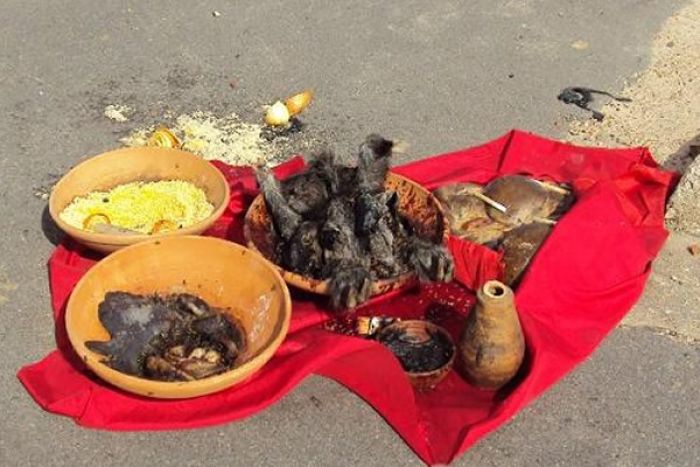
‘More than 50 victims were forced to drink this mysterious liquid which, according to traditional healers, proves whether or not a person practices witchcraft,’ said Filemone.
Belief in witchcraft is still common in some rural communities, despite a strong opposition from the church in the predominantly Catholic former Portuguese colony.

About 50 people have died in Angola after being forced to drink an herbal potion to prove they were not sorcerers (File image)

Angola does not have laws against witchcraft, leaving communities to deal with the issue as they see fit
The deaths were confirmed by police that said 50 people were killed.
‘It’s a widespread practice to make people drink the supposed poison because of the belief in witchcraft,’ provincial police spokesman Antonio Hossi told the broadcaster, warning cases were on the rise.
Angola does not have laws against witchcraft, leaving communities to deal with the issue as they see fit.
Allegations of sorcery are often settled by traditional healers, or ‘marabouts’, by having the accused ingest a toxic herbal drink called ‘Mbulungo’. Death is thought to prove guilt.