Warning: the following story and accompanying photo may upset people because of their graphic nature (FVDK).
I post the following article ‘as it is‘: I have virtually no comments – neither do I confirm the truthfulness of the incident reported nor do I present or suggest my belief in the superstition which forms the base and background of the alleged act, bizarre as it is.
Interesting though (and justifying its inclusion on this site) is the reference to a 2015 study of ritual murders in Vhembe, South Africa. Vhembe is situated in the Northern part of Limpopo Province, sharing borders with Zimbabwe in the north, Mozambique through Kruger National Park in the east and Botswana in the north west. Limpopo Province is notoriously known for its ritualistic murders and superstition.

Reportedly, Dr Alunamutwe Enos Randitsheni wrote a thesis on ritual murders – ‘muti’ murders – while doing his PhD at the University of Venda, and actually said that evil people who believed in such weird practices, such as sucking out someone’s blood, did in fact exist. (italics added by the webmaster FVDK).
“They don’t only exist in Vhembe, but they exist all over the world, and most of them perform these rituals for various reasons but mostly for personal gains,” Dr Dr Alunamutwe Enos Randitsheni alleged, adding that the Tshivenda name for such people was madzhavhathu (cannibals). According to Dr Alunamutwe Enos Randitsheni, most victims are women, children, and people living with albinism.
(FVDK)
‘Vampire’ who attacks old lady killed by angry mob
Published: June 7, 2024
By: Zoutnet, South Africa
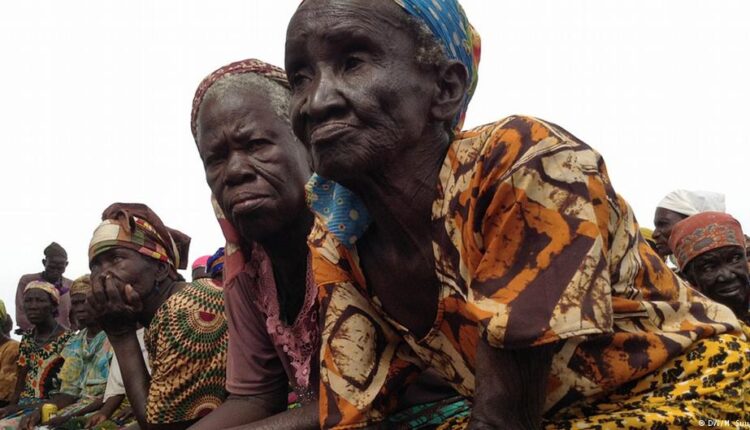
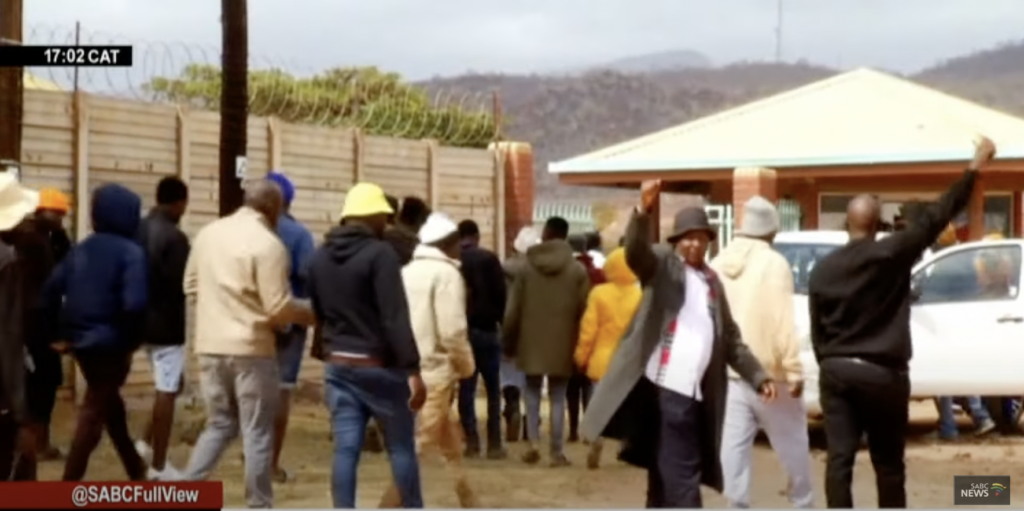
A wave of fear and panic has gripped Vhembe District as reports of alleged vampire attacks have surfaced, leading to tragic and violent responses from local communities. In a recent shocking incident, a man accused of being a vampire was beaten to death and burnt by residents of Shikunduville in the Saselamani area.
The tragedy unfolded on Sunday, 26 May, when a man, after reportedly biting an elderly woman on the mouth in Shikunduville, was accused of being a vampire. The woman’s screams for help drew the attention of other members of the community, who rushed to her aid. In their attempt to rescue the victim, the crowd turned their fury on the alleged attacker.
Despite their assault, the man continued his attack, displaying unusual resistance to the beating. The escalating violence culminated in the community’s beating him to death and subsequently burning his body. The traumatic event has left the residents of Shikunduville deeply unsettled and fearful.
The chairperson of the SANCO branch in Saselamani B, Mr Solomon Mathonsi, said the community was still living in fear. “I was at church that Sunday, so I did not see the incident as it unfolded. I was told that the deceased, who worked at a local farm, was going to send money to his family in Mozambique when he started fighting with one of his relatives. He ran away and tried to get inside a neighbour’s house, and a dog attacked him, which forced him to run to another neighbour. He allegedly threatened her that he would bite her and rape her. He attacked her severely, injuring her face, and she looks scary now. Her mouth looks like it is about to be removed, and she appears as if she was attacked by a vicious animal. When the mob was fighting against him, he was roaring like an animal. He looked like he was possessed by evil spirits. We are now left in fear, both young and old,” he said.
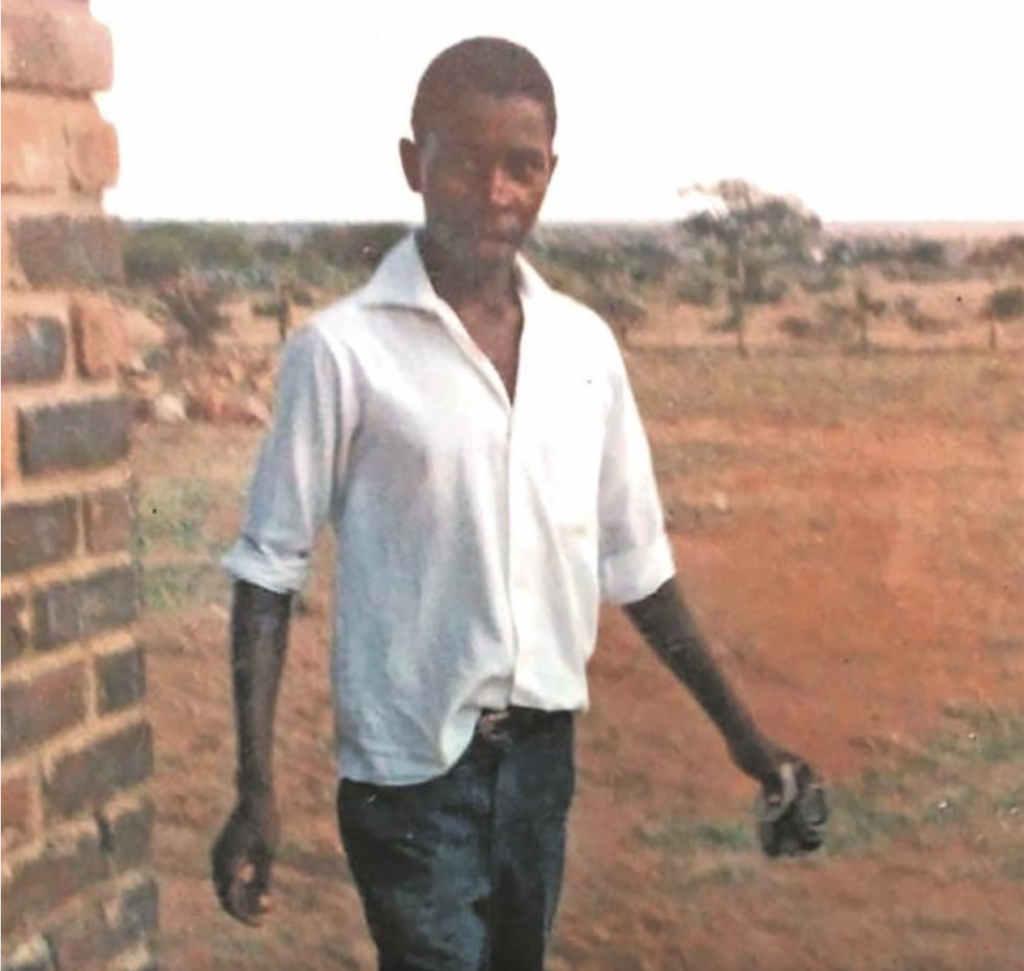
According to the police spokesperson in Vhembe, W/O Vuledzani Dathi, the police in Saselamani opened a murder docket after a 29-year-old man was allegedly killed by the community in Shikunduville. He confirmed that the man had been accused of attacking an elderly woman on Sunday, 26 May.
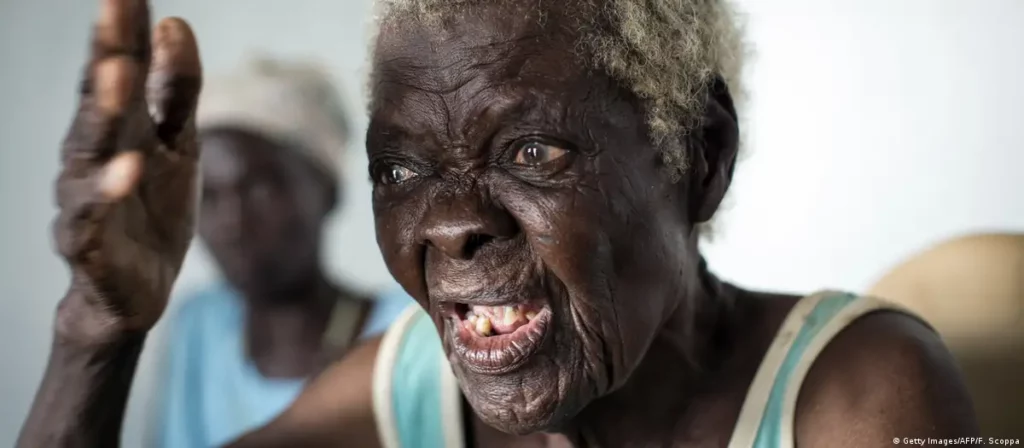
“The police went to house no. 401 in Shikunduville and found the owner, Mr Sam Maceke. The deceased was lying on the ground, wearing black shorts and a black T-shirt. He had injuries on the face and legs. He was tied up with a rope. Mr Maceke told the police that his mother, old lady Nwajaki Priscinah Chauke, was bitten on the mouth by an unknown male person.”
Dathi said the community members had assaulted the male person and tied him up with a rope. “He died at the scene of the crime. He was later identified as Surprise Maluleke of Maineville, a Mozambican with no passport or legal documents. He is said to have been born around 1995. He was taken to Tshilidzini Hospital’s Forensic Pathology department. No arrests have been made so far, and anyone who can assist the police in apprehending the culprits may contact the investigating officer, Sgt Gunguva, on 082 664 6843,” Dathi said.
A 30-second video of old lady Nwajaki Priscinah Chauke narrating how she was attacked started circulating on social media on Wednesday, 29 May. In the footage, Chauke, who can be seen sitting down, wearing a yellow ANC T-shirt and drinking water, said, “He did this to me because he was roaming around my yard. When I asked him what he was looking for, he quickly turned, pushed me, and got inside my house,” she said, speaking in Xitsonga.
The injured lady is currently recovering from her wounds at home.
The incident incited a lot of fear among community members in Vhembe, with many wondering whether creatures such as vampires really exist in Vhembe.
Dr Alunamutwe Enos Randitsheni, who based his thesis on ritual murders in Vhembe while he was doing his PhD at the University of Venda in 2015, said that, during his investigation, he had found that evil people who believed in such weird practices, such as sucking out someone’s blood, did in fact exist.
“They don’t only exist in Vhembe, but they exist all over the world, and most of them perform these rituals for various reasons but mostly for personal gains,” he said. He said the Tshivenda name for such people was madzhavhathu (cannibals).
He added that most of their victims were women, children, and people living with albinism.

Photo: Video screen shot.
Source: ‘Vampire’ who attacks old lady killed by angry mob