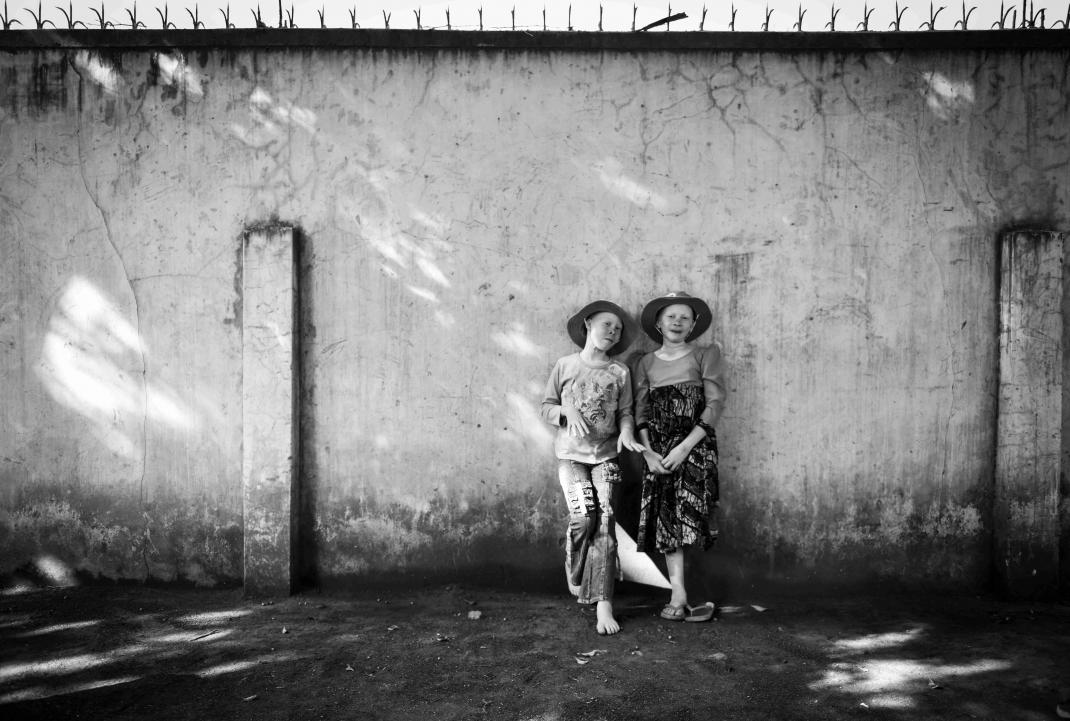
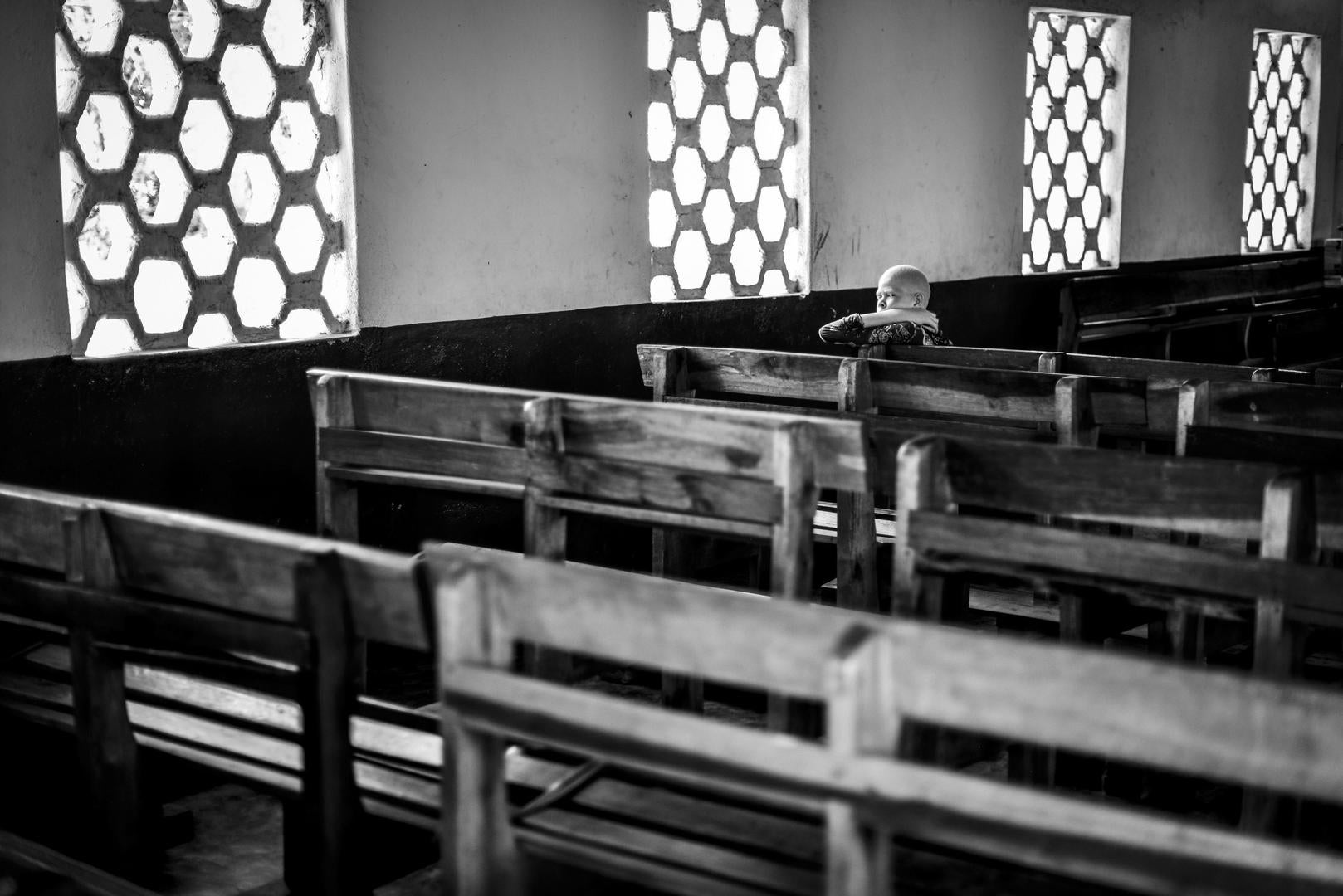
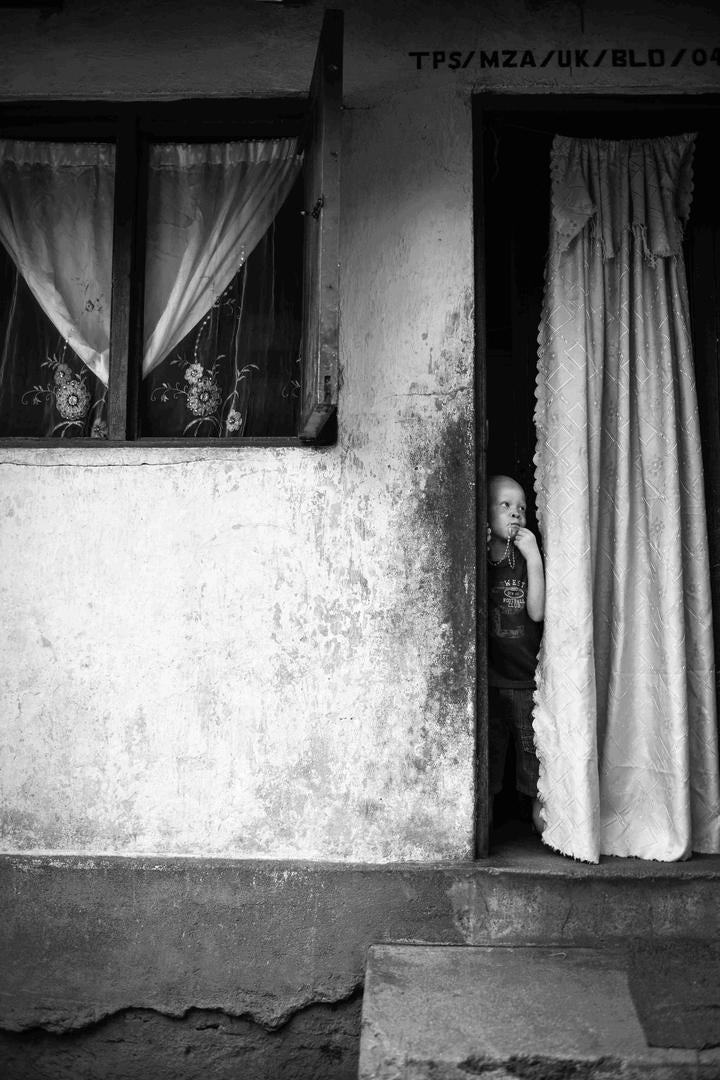
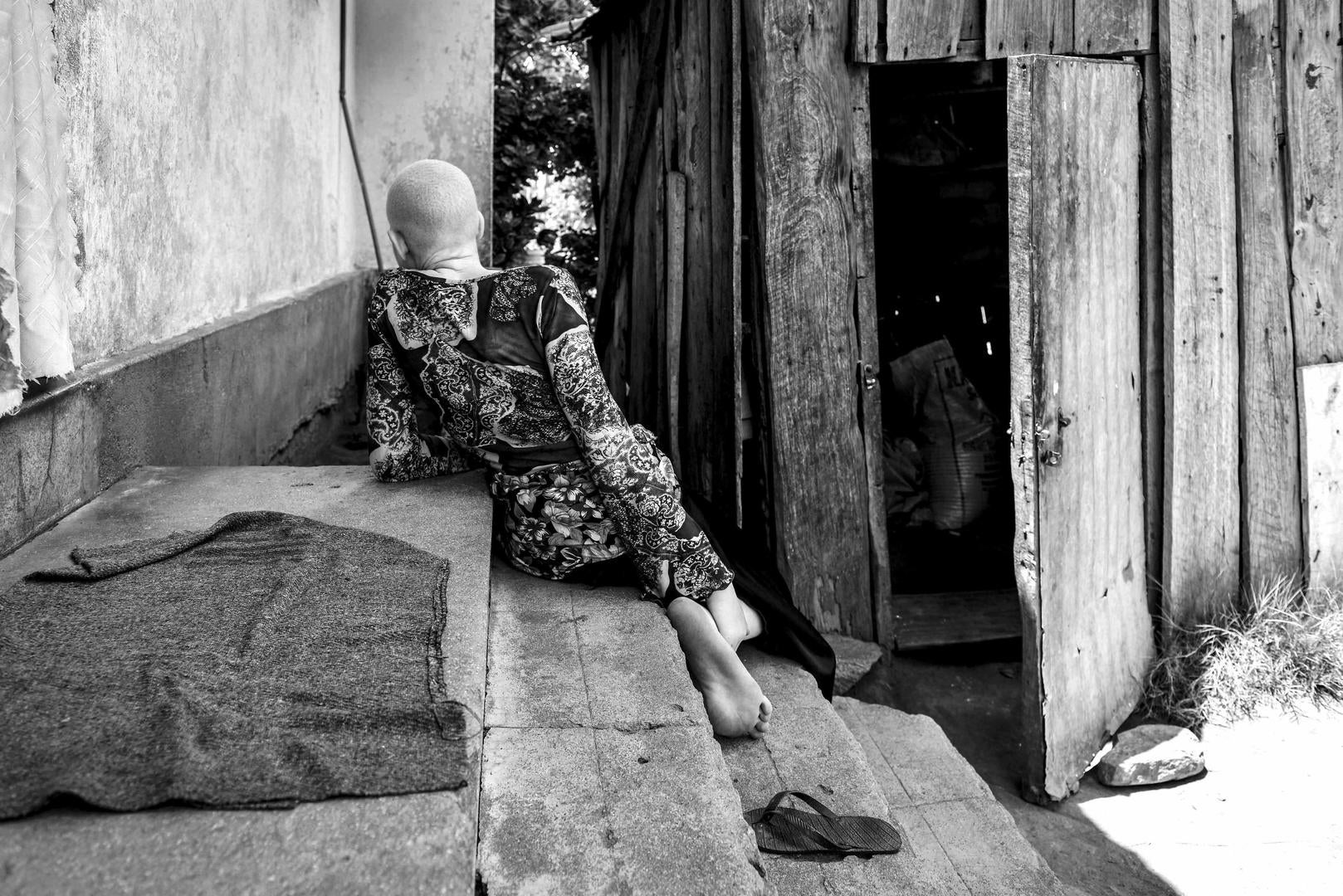
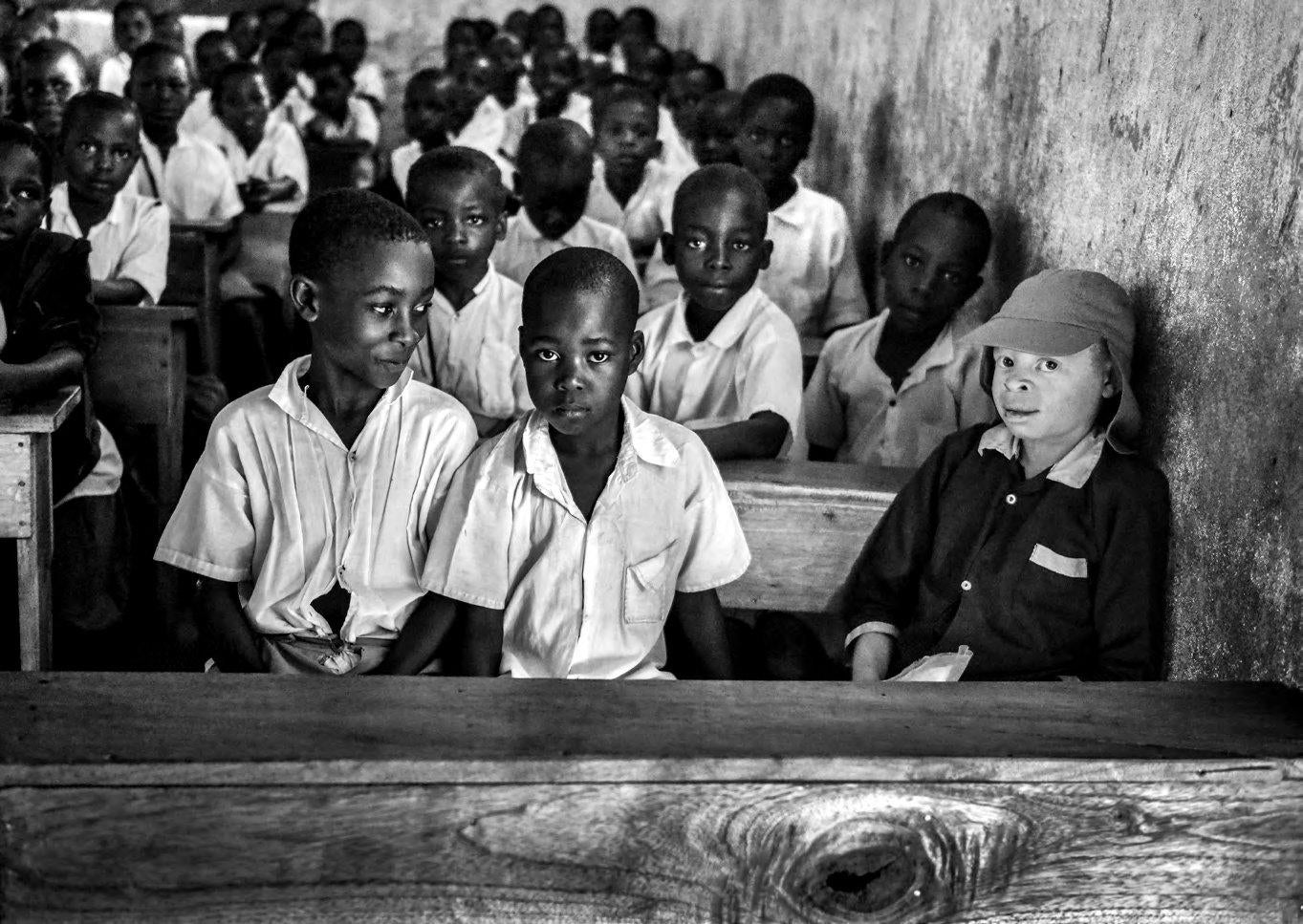
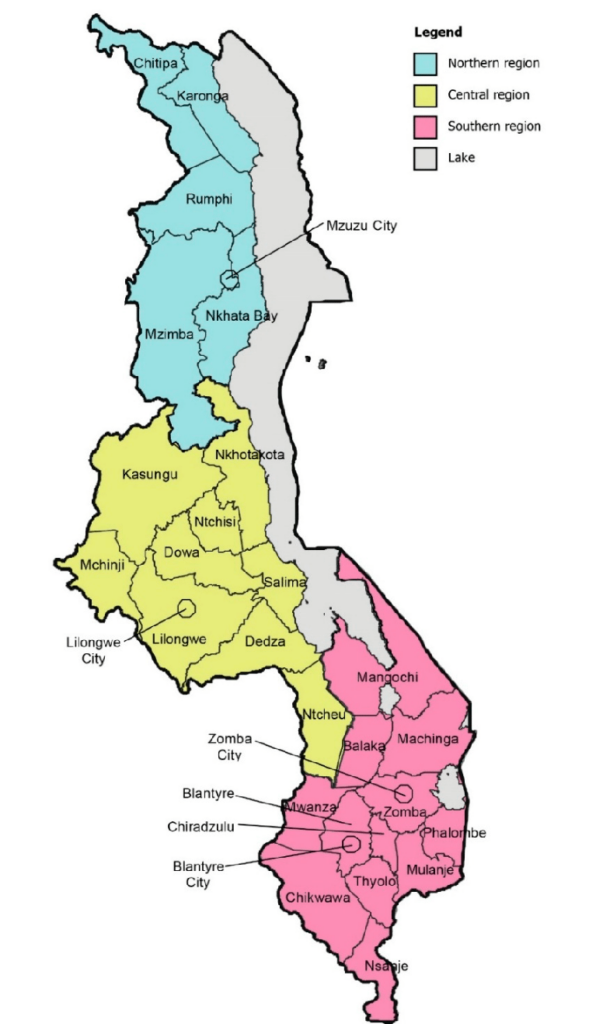
There is hardly any doubt that in Malawi the position of people with albinism is the most fragile and dangerous as compared to other countries in Sub-Saharan Africa. I have repeatedly mentioned this here, see e.g. my posting earlier this year, on January 22.
In 2017, ALJAZEERA reported that In Malawi, more than 115 people had been attacked in the past two years and that at least 20 of them did not survive the attack. Below follows an extensive report of ALJAZEERA on the victims, the survivors and the perpetrators (as far as known).
ALJAZEERA is to be commended for raising awareness on the human rights violations people with albinism experience and the efforts being made to protect them.
ALJAZEERA is to be commended for this excellent work of investigative journalism and the attention thus paid to this curse. People with albinism face discrimination in at least 23 African countries. For many, this discrimination amounts to insecurity, violence & murder.
Also in the current year, ALJAZEERA paid attention to the plight of people with albinism, on June 13, International Albinism Awareness Day, with a series of tweets. Click here to access the tweets.
Warning: some readers may find the following stories disturbing (webmaster FVDK).

Published: June 13, 2022
By: ALJAZEERA
Killed for their bones – On the trail of the trade in human body parts
In Malawi, people with albinism are being killed and their bodies harvested; children and adults hacked to death with machetes and kitchen knives. More than 115 people have been attacked in the past two years, at least 20, fatally. Those who have survived have been left with deep physical and psychological scars, and remain fearful that those who hunt them will return.
But why is this happening? Ask and most people will talk about an elusive market for these body parts, people who are prepared to pay large sums of money for them and witch doctors who use them in potions to cure everything from disease to bad luck. But few seem to know where this trade actually takes place or to be able to point to an instance of money changing hands.
So, does this market of human body parts really exist, or is it a myth that is driving murder? We went in search of the market and found a toxic mix of witchcraft, poverty and desperation.
Here are the stories of the victims, the survivors and the perpetrators.
The condition that makes me black without black, white but not white. That is how it was, and I will tell you all about it. – Petina Gappah, The Book of Memory
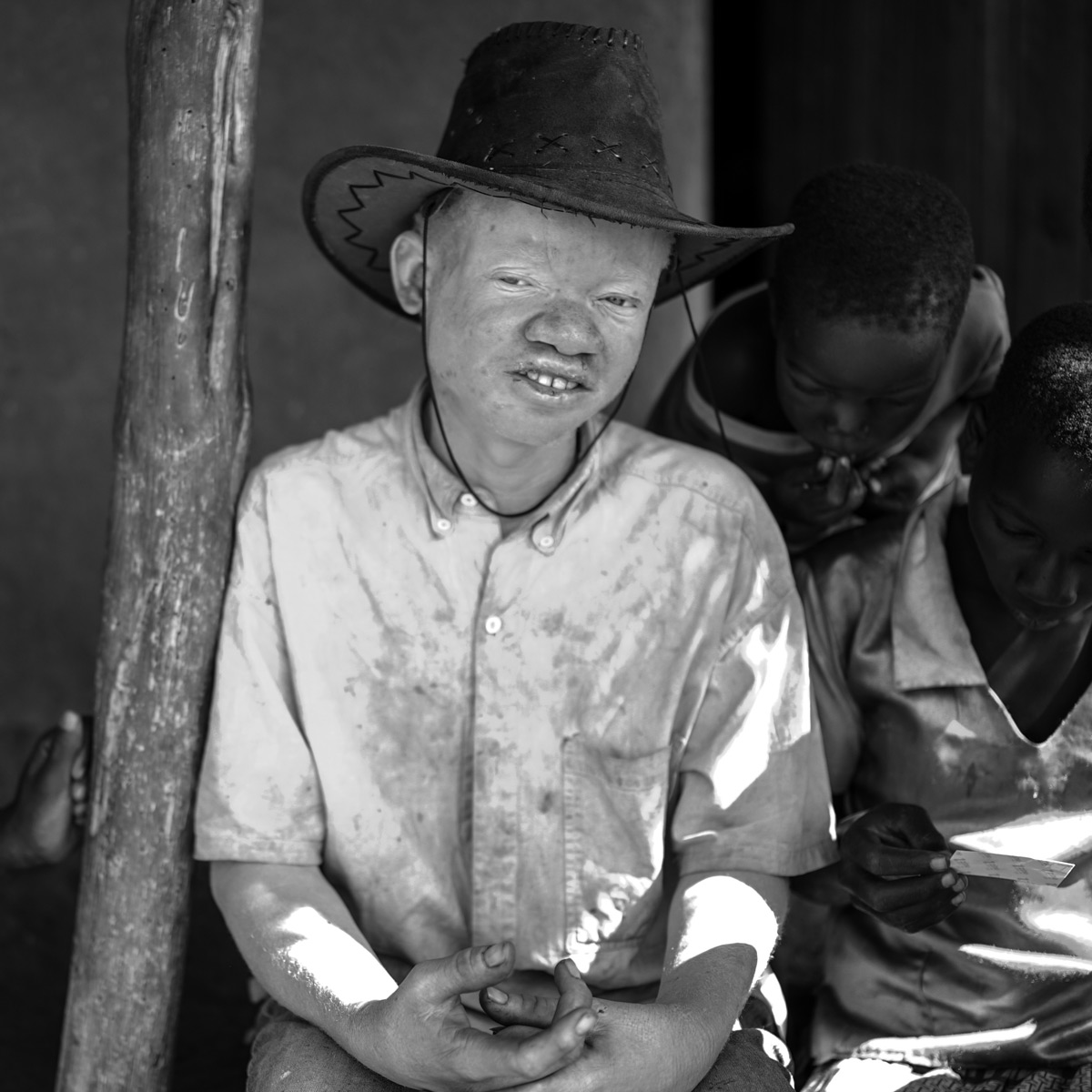

1 – The Victims
David’s story
Village of Nambilikira, Dedza district, eastern Malawi
It was a Sunday in April 2016. A warm, dry day. Seventeen-year-old David Fletcher was being moody and withdrawn. He wanted to watch a football match at the local school instead of helping his family gather maize in the fields. His parents eventually relented and let him go.
When he didn’t return later that day, they searched the village, but couldn’t find David.
The next day, they walked to the nearest police station to report him missing. Then they waited.
A week later, the local police chief came to their home to deliver the news: David’s dismembered body had been found, 80km away, in neighbouring Mozambique. It was badly decomposed, he told them. It couldn’t be brought to the village for burial, but he could bring the arms and legs, if they wished. And if the family could afford the journey, they could visit it where it was found.
“He was dead. What benefit was there to see his dead body?” Fletcher Machinjiri, David’s 65-year-old father, asks, dismissively. “It was too expensive for us.”
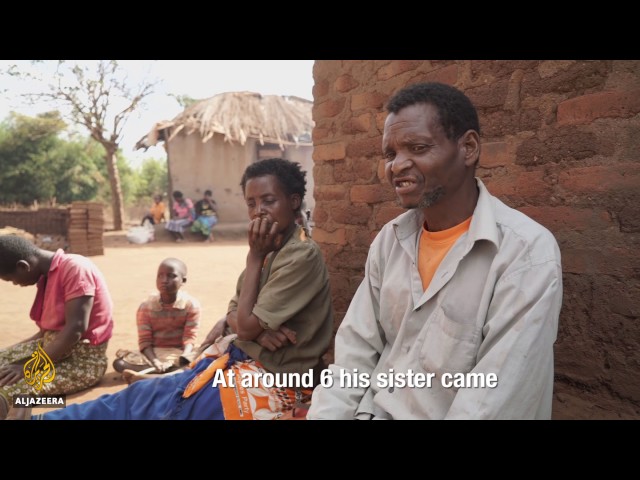

Fletcher is sitting outside his house. His 53-year-old wife, Namvaleni Lokechi, sits beside him. Her face is expressionless. Their 32-year-old daughter Mudelanji and 21-year-old son Manchinjiri sit on the hard earth a few metres away. They listen as though it is the first time they have heard the story.
“He was killed like a goat at a market,” Lokechi says, staring into the distance. “His arms and legs had been chopped off. They broke off some of his bones. His skin was hanging. And they buried him in a shallow grave.”
He was killed like a goat at a market. His arms and legs had been chopped off.– Namvaleni Lokechi, the mother of David Fletcher, a murdered 17-year-old
She makes chopping motions with her hands as she speaks.
“We cry every day,” Fletcher says. “To us, he was a ray of hope. We believed in his future. We thought he would lift our hand because he was good at school.”
“We still battle to eat without him.”
‘A war against people with albinism’

Born in 1999, David was the fourth of five siblings – and the only one to have been born with albinism.
“I wasn’t surprised when he was born,” David’s mother says softly. “I was more than happy with his complexion.”
Her tiny frame stiffens when she talks about her son.
She had an aunt in Blantyre with the same congenital disorder that results in a partial absence of pigmentation in the skin, hair and eyes, she explains.
“I’ve always felt that this group of people were lucky in life,” she says slowly.
David was a star pupil at the local school in the neighbouring village of Kachule.
His teacher, Clement Gweza, recalls feeling mildly concerned when he didn’t turn up for school that Monday.
“I thought maybe there were no groceries at home, or maybe he was unwell,” Clement says, sitting inside his empty classroom. “But the second day [he didn’t turn up] … then I got worried.”
When he learned what had happened to David, he says, he was shocked. “It meant I was next,” he says, placing his hands on his chest.
For Clement also has albinism.

So, too, does 14-year-old Latida Macho, another pupil at the school. She is one of five siblings with the condition. After David’s murder, her family refused to send her to school for three weeks.
“If this is war against people with albinism, then it means I’m second in line,” Clement reflects.
He says he knew that people with albinism were being murdered, but “for it to happen in the district, but also in my class, it was unreal”.
Within days, two men were arrested for the murder.
Both Malawians, they were tried in a district court in May 2016 and sentenced to 25 years in prison for conspiracy to commit a crime and abduction.
David’s family say they heard about the arrests and subsequent trial only from the media. And that they are bitterly disappointed with the outcome.
“The accused persons should be killed as well,” Fletcher says, pointing to the floor. “The child was brutally killed, hence they must equally be killed brutally.”
Alfred’s story
Village of Nasi, district of Phalombe, eastern Malawi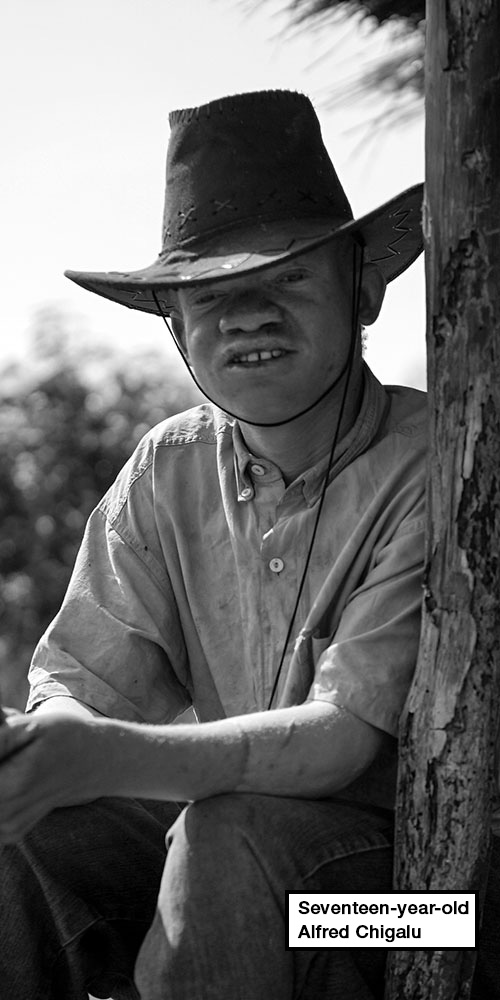
Seventeen-year-old Alfred Chigalu lives with his aunt in a mud home surrounded by dead sunflowers.
Their courtyard of red earth is home to five goats and a dozen raucous chickens.
The nearest neighbour is a five-minute walk away, along a path cut through overgrown grass. It takes 20 minutes – across dried up tobacco fields – to reach the main road. Drought has hit this region hard, and while tall mango trees provide shade for the farmers, they bear no fruit.
The climate here is harsh. Crops are often destroyed by drought or violent hailstorms. Like others in the village, Alfred and his aunt, Lydia Petulo, are surviving on pieces of dried maize from last year’s harvest. The goats in the yard are not their own. Lydia looks after them for a local merchant, and receives one at the end of each year in return.
In December 2015, four men broke down the door of Alfred’s bedroom while he was sleeping. They slashed at him with machetes, hitting the back of his head, his shoulders and his back. They tried to drag him out of the house. When his aunt found him in a pool of his own blood, his attackers ran away.
Alfred survived but was left badly scarred.
Now, the slightest sound wakes him, and when he walks to the village he must be accompanied.
“Before the attack I used to depend on him; I could send him to the market, he could go to the farm and do the farming,” Lydia says, biting her lips as she completes her sentences.
“But I cannot do the same these days.”
“I fear for his life. The responsibility has shifted to me.”
But this isn’t the first time she has been afraid for her nephew. She took him out of school six years ago, when the taunting began, she explains.
Lydia slouches as she narrates their story. Her tired eyes wander. But they brighten when she talks about Alfred. She adopted him after his mother – her sister – died.
Alfred had a sibling who also had albinism, but that child died, she recalls. She doesn’t remember the dates or the details – of his sibling’s or his parents’ deaths – other than that both of Alfred’s parents died around the time he took his first steps.
‘I am lonely’
Alfred is sitting outside on the floor, his back against the house, wearing oversized jeans and a short-sleeved shirt. They are the only clothes he owns. He was wearing his other outfit when he was attacked. There was so much blood that it had to be burned.
On his head is a large cowboy hat. 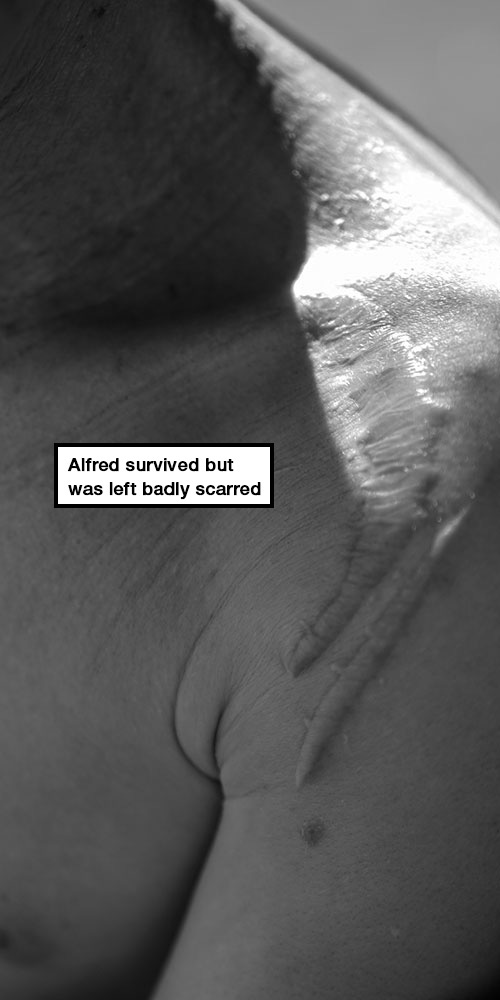
He is tall with broad shoulders that droop when he walks. For the first few hours that we are there, he doesn’t talk.
But when we put the camera away and move out of sight of the curious neighbours who have gathered to watch, he begins to speak.
His parched lips barely move.
“I wake up at 6 in the morning, every day. I sweep the yard, but I feel pain in my arms,” he says slowly.
He removes his shirt to reveal long, deep scars on his chest and back.
“The way they cut me, they cut my veins. I can barely hold a hoe,” he explains.
I want to finish school, to become a teacher, and move out of here. I would love if someone could take me away from this village. I have to get out of this place.– Seventeen-year-old Alfred Chigalu, who was attacked in November 2015
When she found him on the floor, Lydia began to scream and cry.
“The neighbours came, but it was too late, the attackers had left,” she says. “I really felt sorry for him when I looked at him and I knew he was lucky to have survived. He would have been killed if he hadn’t screamed for me.”
She says she knows why he was attacked.
“Before the attack, some people used to mock him if he went outside the house. They [would say] he is worth millions of kwacha [thousands of dollars], so that gave us an indication that his life could be in danger,” Lydia explains.
The physical wounds have mostly healed, but life is not the same for Alfred. He misses “chatting”, he says, shyly, before adding: “Most of all I miss my friends. I am lonely.”
His aunt says he “lacks peace”.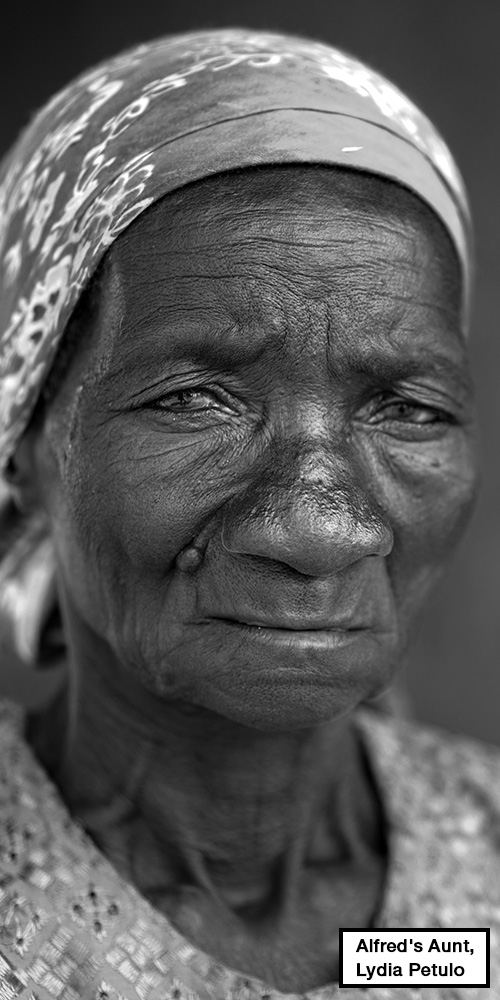
In April 2016, Ikponwosa Ero, the UN’s independent expert on the enjoyment of human rights by persons with albinism, visited Alfred and his aunt. She told Al Jazeera that Alfred seemed to have suffered “memory loss” after the attack. But when we visit him two months later, he rolls off the names of towns in Malawi, capital cities of African countries and national political leaders. He seems to be recovering.
Fiddling with a piece of dry hay, he tells us: “I want to finish school, to become a teacher, and move out of here. I would love if someone could take me away from this village. I have to get out of this place.”
Hari’s story
Village of Mpakati, Machinga district, southern Malawi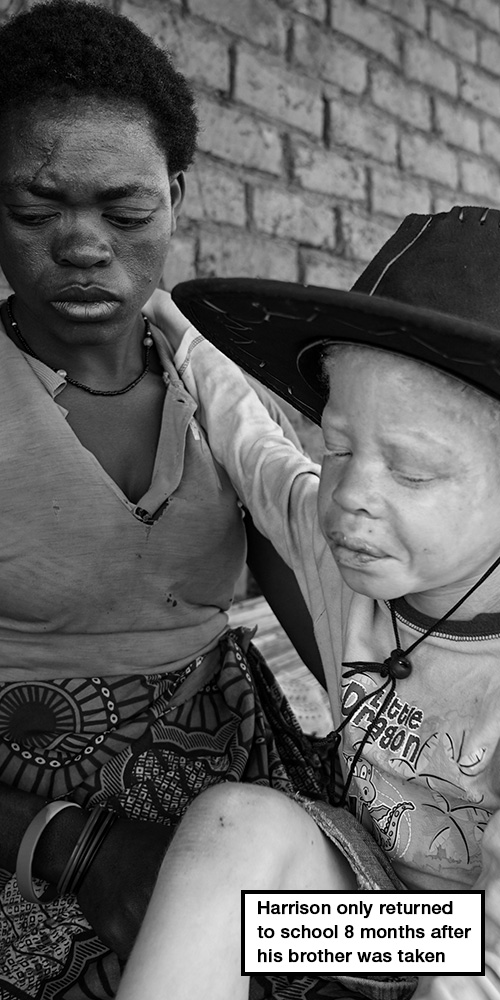
Edna Cedric remembers that night in February 2016.
Her husband, Marizane Kapiri, had gone fishing. Her identical nine-year-old twins, Hari and Harrison, were sleeping beside her.
She heard a knock at the door. When she answered it, a machete-wielding man barged inside, slashing at her.
He pulled Hari from the bed and dragged him to the door. Edna tried to hold on to him while also gripping Harrison with her other hand.
Then the intruder struck her face with the machete and she fell to the floor. And, just like that, her son was gone.
The police brought the head wrapped in a cloth and in a sack. His mother identified it.– Marizane Kapiri, Hari’s stepfather
“I couldn’t hold on to him any longer,” she says, quietly. “I ran out screaming.”
“Four days later, the police found his head in Mozambique.”
“The place was very lonely. This is why we moved here,” her husband says.
The fisherman is not the father of Edna’s children. He says he spent the best part of the five days after Hari was abducted explaining to the police why he wasn’t at home when the attack took place. They suspected that he was involved and it wasn’t until the village chief explained to them that he spent much of his time at the lake, catching fish to feed the family, that the police let him go.
“After the police discovered the head, they sent a message to us that we should be ready to see it,” Marizane explains. “They brought the head wrapped in a cloth and in a sack. His mother identified it.”
According to Amnesty International, two men were arrested in connection with Hari’s murder. One was said to be an uncle, and the other a stranger who had an existing conviction for possessing the bones of a person with albinism. For that crime, he had been fined $30.
The family, though, say they have no idea who was responsible for the attack and what has become of those who were arrested.
The twin brother
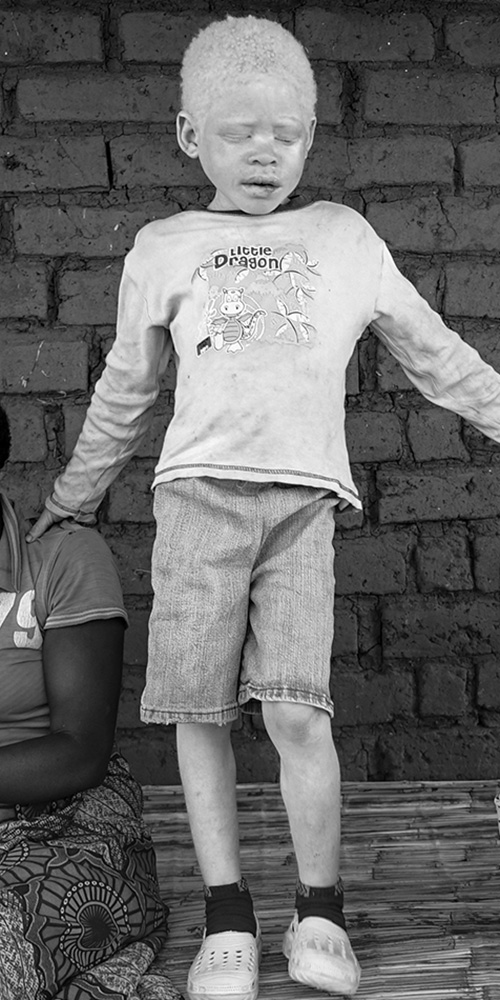

Harrison is wearing pyjamas and a cowboy hat. He sits between his parents as they take turns to talk. He fiddles with the cords of his hat, licks his cracked lips and scratches at the dry skin on his arms. He only returned to school in September 2016, eight months after his brother was taken.
Their mudbrick home is in a remote rural area, far from the main road between Blantyre and Mangochi. Houses here sit in small plots on expansive fields. It is a few minutes’ walk to the nearest neighbours through fields of browning plants that haven’t been harvested in a year. Here, police officers are few and far between.
But this is not where Hari was taken from. That home was even more isolated, Marizane explains.
“We demolished the house … and moved here so we are closer to other people,” he says.
But the move hasn’t changed much for the remaining brother, Harrison.
“He wakes up in the middle of night, screaming, because he can’t find his brother. We just tell him he will come back one day,” Marizane explains.
He wakes up in the middle of night, screaming, because he can’t find his brother.– Marizane Kapiri, whose stepson, Hari, was murdered
Edna says that she can’t get over the pain she felt when she saw Hari’s head.
“I immediately thought about his brother, Harrison, and I knew his life would never be the same,” she says, looking at her surviving son.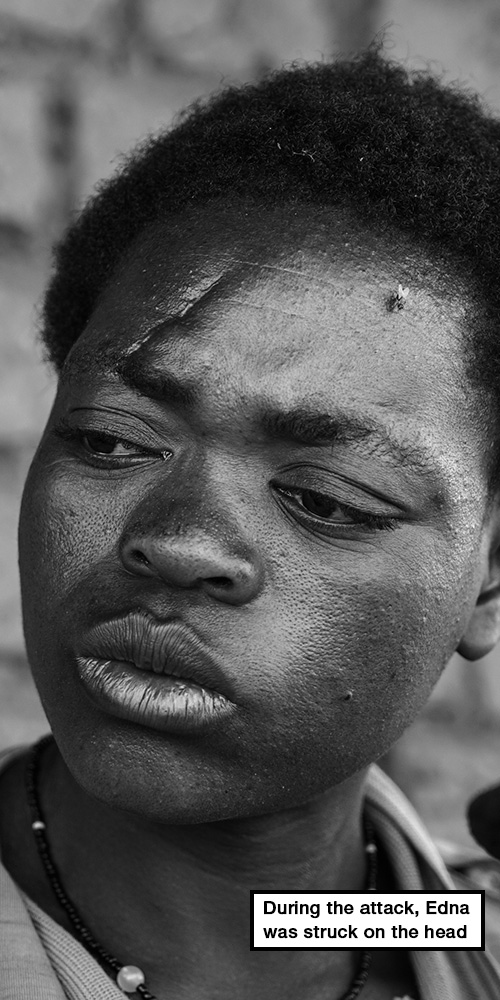

2 – A History of Violence
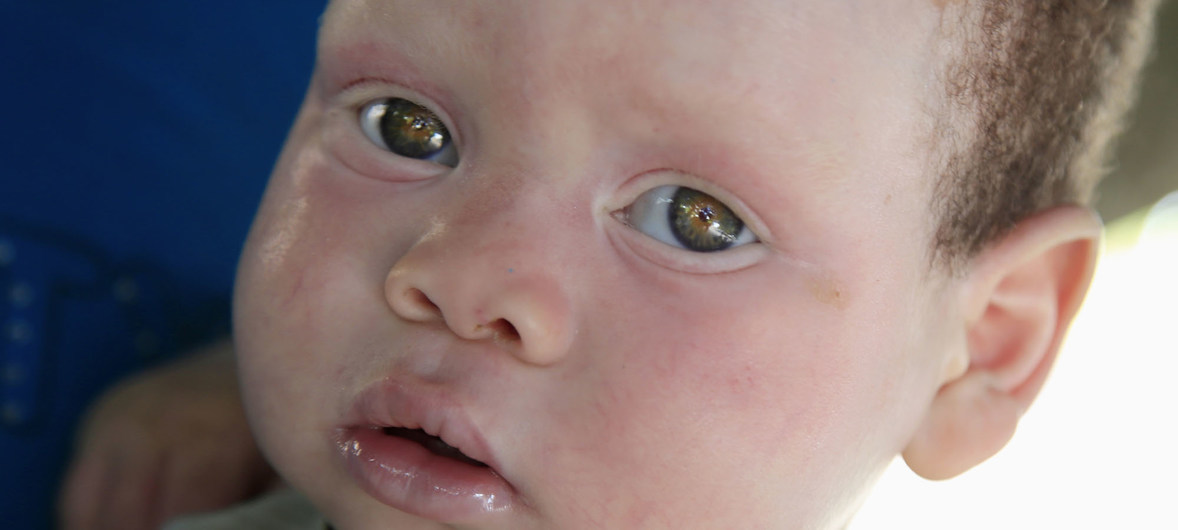
Borrowed from the word “albus”, meaning white in Latin, albinism is a congenital disorder where the body is unable to create enough melanin to darken the skin, hair and eyes.
The non-contagious condition affects about one in 20,000 people worldwide. But it is more common in sub-Saharan Africa, where one in 5,000 have albinism. Most cases are in Mozambique, Tanzania, Burundi, Kenya, Zimbabwe and South Africa.
In Malawi, a country of 16.5 million people, there are said to be 7,000 to 10,000 people with albinism.
Why it affects this part of the world so disproportionately is unclear.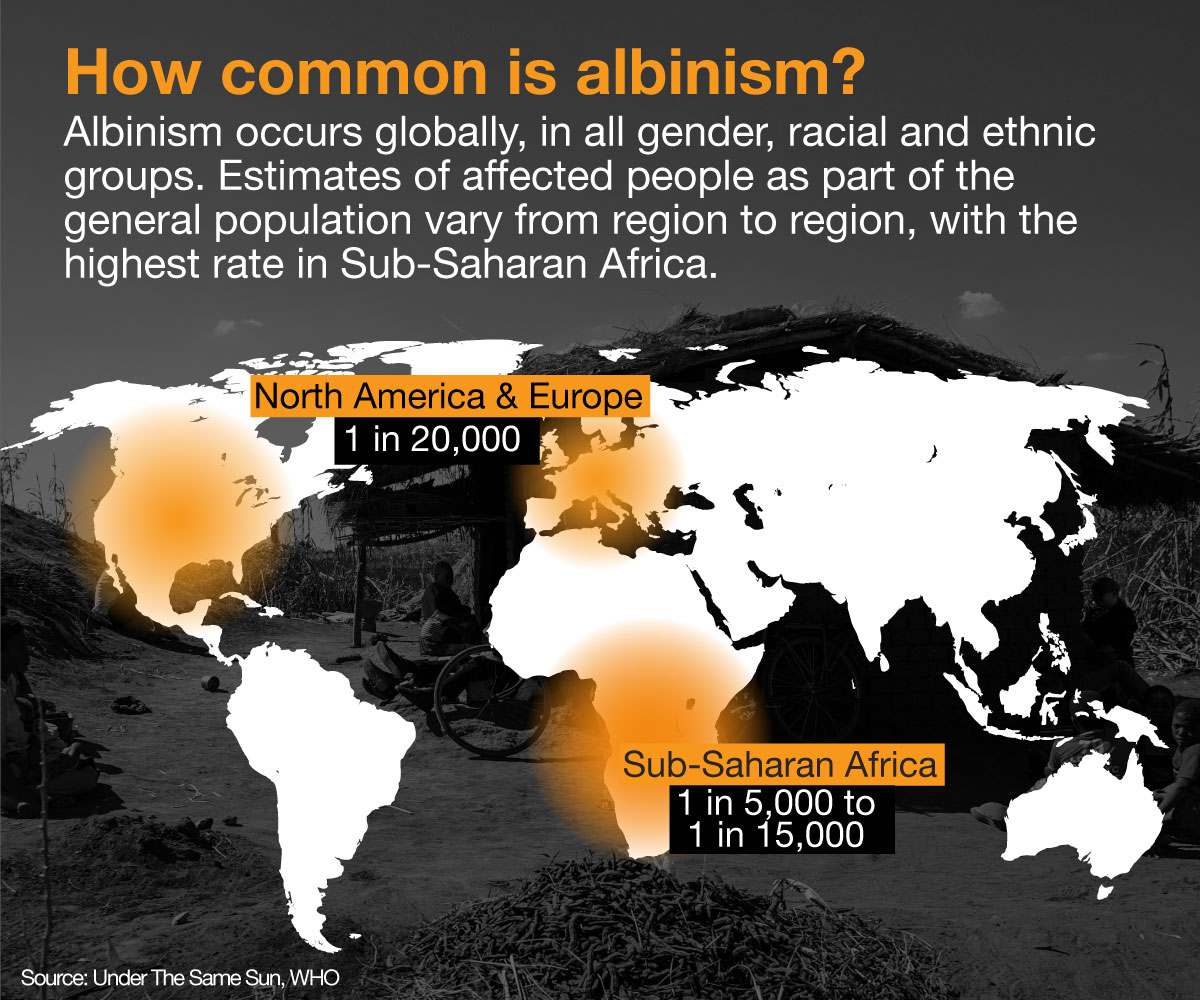
And it is not just a matter of colour: lack of melanin often results in poor vision and sensitivity to light. In fact, many people with albinism are legally blind.
Because their skin is particularly vulnerable to the sun’s ultraviolet rays, they can also be predisposed to skin cancer and lesions.
According to a 2014 study, people with albinism in Africa are 1,000 times more likely to get skin cancer than others.
But their plight is not solely medical.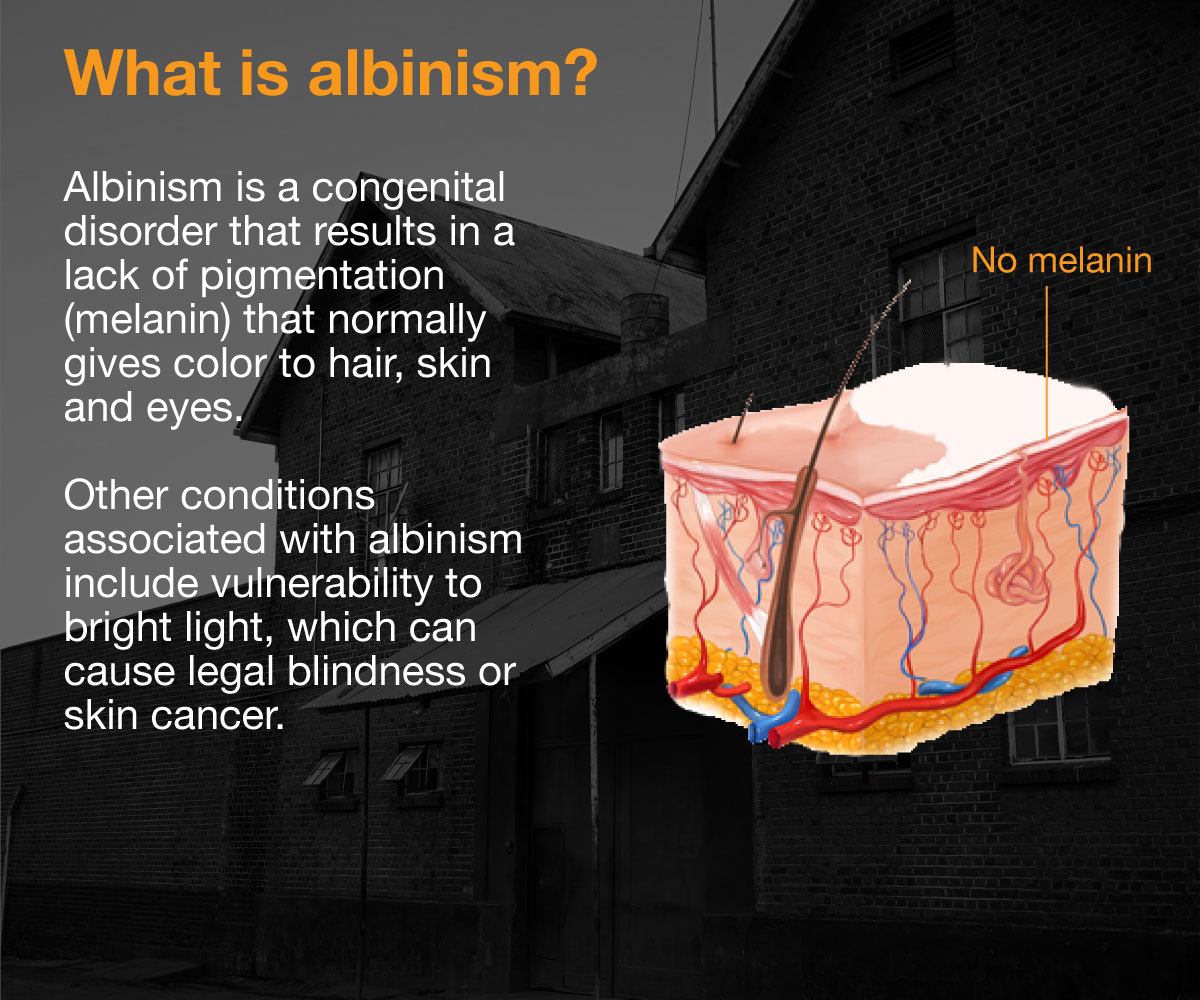
The story of discrimination against people with albinism is an old but not necessarily well-documented one. It is driven by myths and superstition.
According to Amnesty International, those with albinism face discrimination in 23 countries in Africa.
For many, this discrimination amounts to violence – murder, infanticide and live burials.
The past decade has seen an increase in the number of documented killings and maimings of people with the condition, driven in part by a belief that their organs, bones and body parts can be sold on the black market.
And that belief is fed by the myth that their bones are made of gold dust and the suggestion that they are a necessary component of magic potions.
But while there are reports of bones reaching up to $75,000 on the black market, there have been no documented cases of money changing hands. So the question of whether an organised trade in the body parts of people with albinism exists has yet to be definitively answered.
The UN’s Ikponwosa Ero says they have been unable to confirm the existence of a market.
“There is allegedly a lot of money in this business. And I say allegedly because people keep on repeating the idea that there is a lot of money in this, and it would seem that the media is part of the reason some people have gotten involved,” she says. “But then some countries have witnessed a reduction in the number of attacks, maybe because people are realising there is no value [in the bones and body parts].”
The majority of the documented attacks have taken place in the Great Lakes region, particularly Tanzania and Burundi. According to media reports, Tanzania has seen some 180 attacks, including 76 murders, since 2000. Thirty-five of those murders took place in 2015.
Within eight months of her appointment as the UN’s independent expert on albinism in June 2015, Ikponwosa, who herself has albinism, documented 40 attacks in eight countries.
Although there has long been discrimination, she points to a more recent phenomenon: “Hacking people [with albinism] alive.”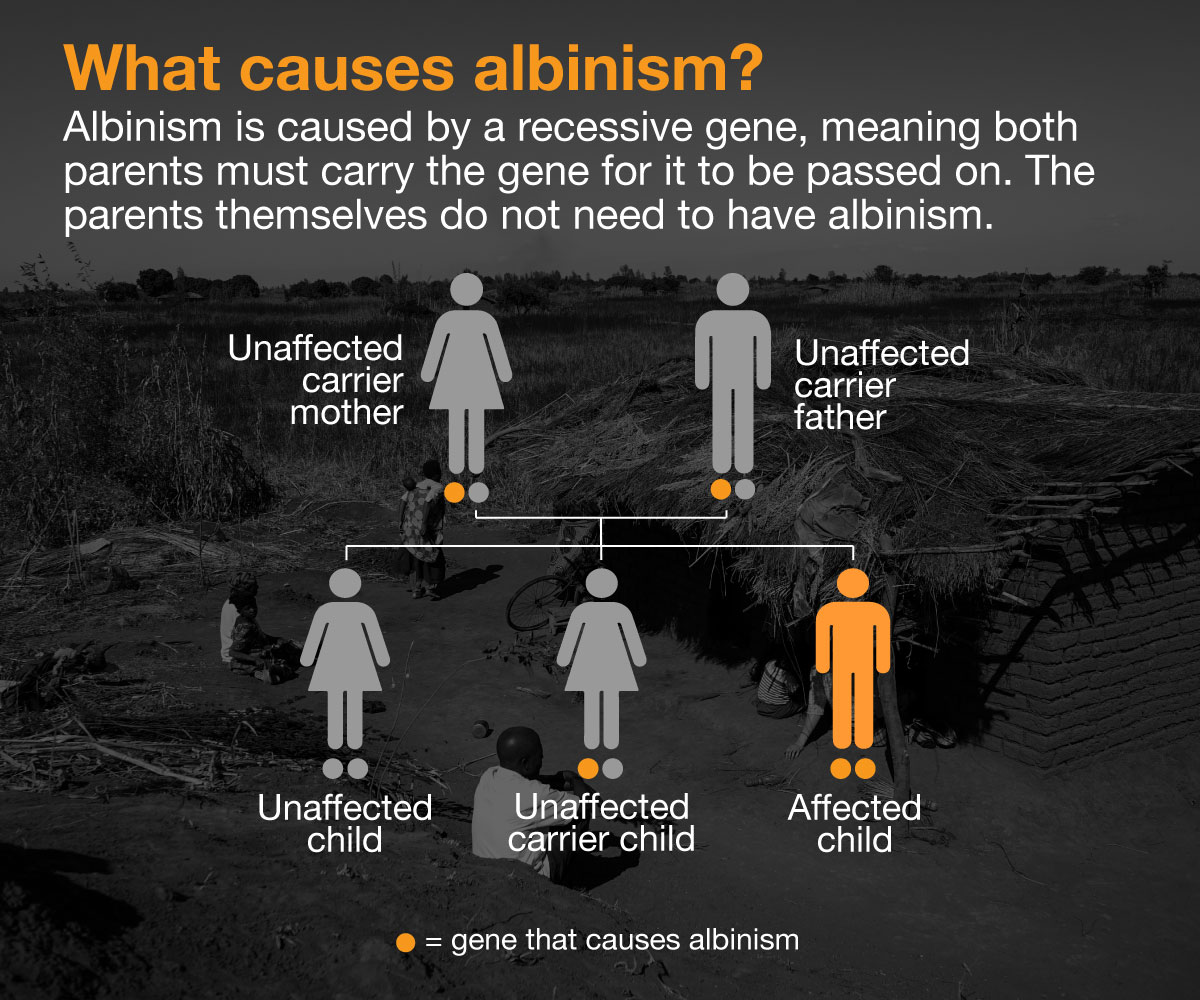
‘Millions, millions’
Zomba, southern Malawi
Emily Chiumia works at a government department in Zomba, southern Malawi. But she moonlights as an activist for people with albinism.
She’s happy to talk, even if the topic is the names they call her.
“You walk on the street, and they call you ‘millions, millions’,” she laughs, “as if we are gold.”
Emily is the former vice-president of the Association for Persons with Albinism (APAM). Since the attacks began, Emily and the association have been documenting the offences committed against people like her.
Most of them, she says, are carried out by relatives, neighbours or people the victims considered to be friends.
“Before, it was a case of people saying ‘if you sleep with a person with albinism, your skin will turn white’,” she says. “But now, it’s different. I cannot enjoy my life as I used to … I can’t walk in the evenings, can’t sleep, even at home, I fear who might come.” Her laugh has disappeared now.
You walk on the street, and they call you ‘millions, millions’, as if we are gold.– Emily Chiumia, former vice-president of the Association for Persons with Albinism
Radio DJ Ian Sambota describes how in 2012 he was befriended by an “older, educated” woman who first offered him K100,000 ($138) and then K500,000 ($700) to sleep with her. “She was HIV positive and she thought if she slept with a person with albinism, it would be solved,” he says.
Ian refused, but admits that the offer was tempting because he needed the money to pay for medical care for his mother.
Steven Burgess is in his 40s and says he has been called a “white animal” since he was a child. But this is “a time of crisis”, he explains, referring to the increase in attacks.
Bazirio Kaudzu, 46, says he feels so threatened that he only travels to the clinic in the capital Lilongwe – to collect the zinc oxide ointment needed to treat the lesions and blisters on his skin – if his nephew accompanies him. It’s an expensive journey for the tomato farmer, so each month he must take out a loan to cover the cost of the taxi ride for two.
But it hasn’t always been this way.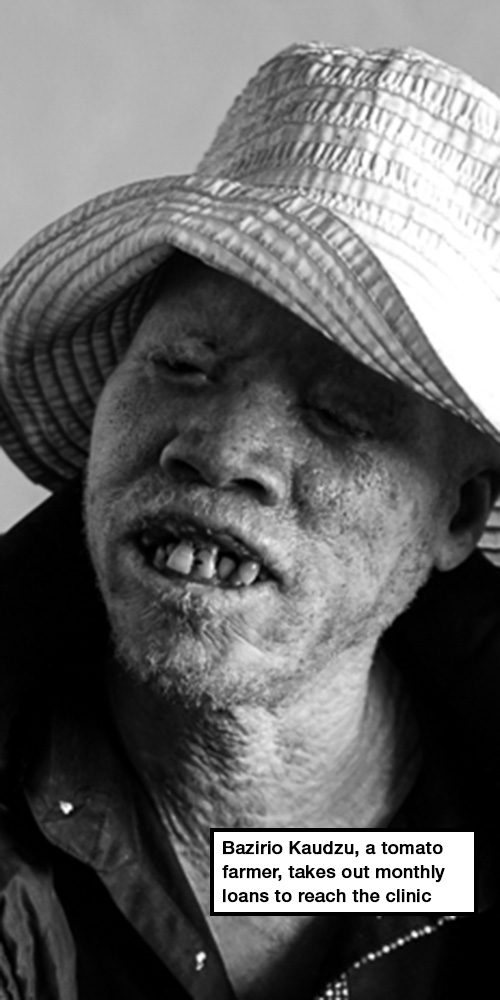
Patricia Maguwa, 37, remembers a time when her husband, gospel singer Geoffrey Zigoma, was considered one of the golden voices of Malawian music. Before he died of cancer in 2013, he always tried to offer a counter-narrative to the misperceptions about people with albinism, she says.
“He was called names like ‘yellow man’, but he never felt insecure about his life,” she says from her modest home 7km outside Lilongwe. “[But] the situation is different now.”
A shifting trade
Malawi’s government recognises that there is a problem.
Neverson Chisiza, a senior state advocate at the Ministry of Justice and Constitutional Affairs, says there have been at least 85 documented cases, including murder, assault, attempted abductions, trafficking, maiming, and grave robberies since 2014. At least 20 of those cases have been murder.
In May 2016, Ikponwosa Ero said that if serious action wasn’t taken to stop the attacks, people with albinism could become extinct in Malawi.
Malawi’s government says a crackdown in neighbouring Tanzania has shifted the “trade” in body parts to their country.
Senior Chief Kawinga, a traditional authority from Malawi’s Machinga district, where most of the attacks have taken place, told us during a visit to his office that he’d heard the market for body parts was in neighbouring Mozambique. Each country in the region tends to posit their neighbour as the source of the problem.
Though many people tend to use the term “albino”, there have been significant attempts to change the terminology to “person with albinism”. Ikponwosa Ero says this is preferred as it puts the person before the condition, while Canadian charity Under the Same Sun points to the fact that albino has historically been used in a derogatory manner.
In June 2016, 150 government officials, academics and activists from 26 countries met in Dar es Salaam for the first forum on albinism in Africa. It aimed to create an action plan to end the attacks, and concluded that governments must dedicate a budget and a multisectoral task force to doing so. It recommended a range of measures and best practices. “Now that we have a catalogue of effective specific measures that are not very expensive to execute, governments should no longer act ignorant of what to do on the issue … It is time to act,” said Ikponwosa Ero.
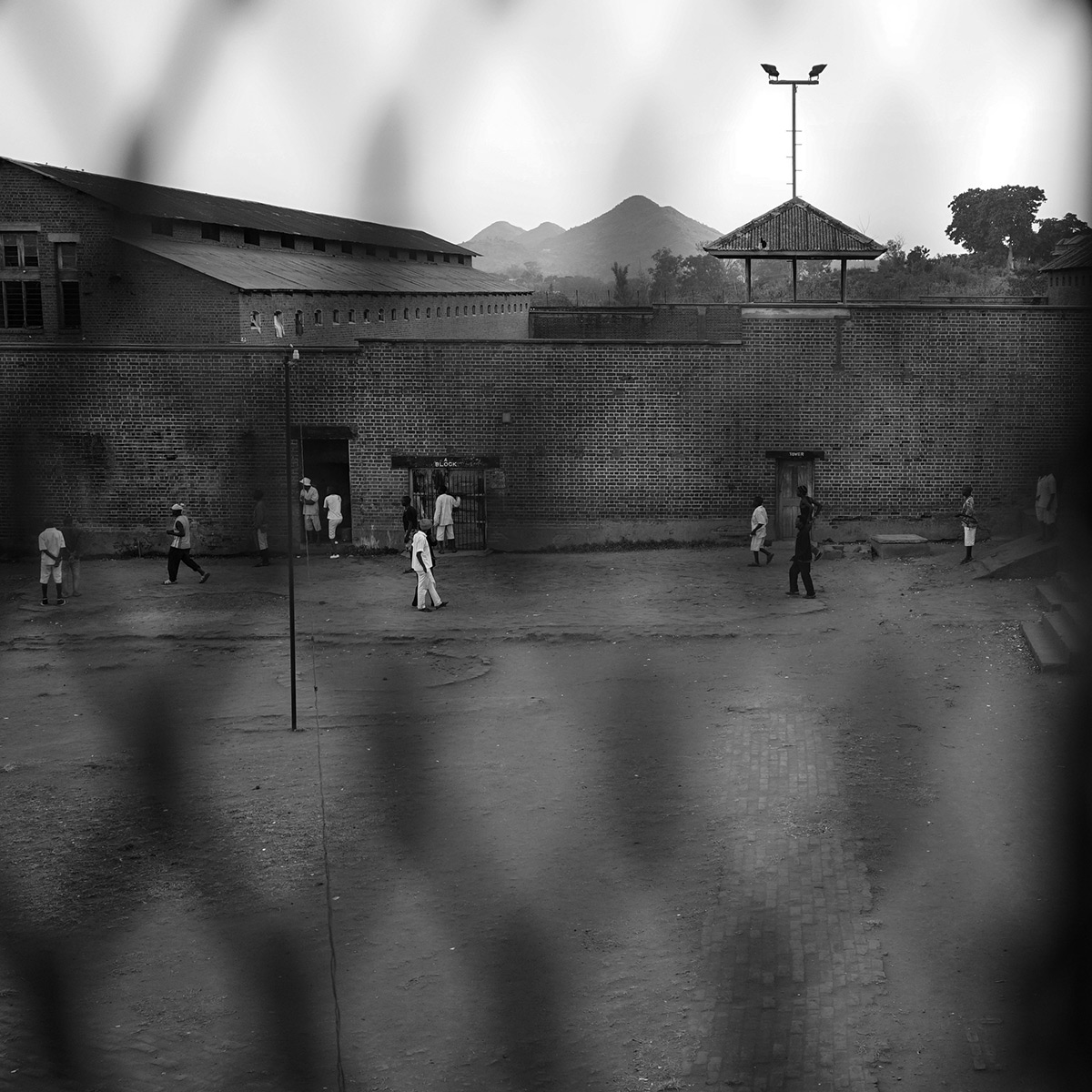

3 – The Perpetrators
Zomba, southern Malawi
The red brick walls glisten in the midday sun.
Zomba Maximum Prison stands like a citadel in the former capital. It might resemble a factory were it not for its watch towers and the metal fence that encircles it. Flanked by mango trees and shrubs, a dirt track leads to the main entrance.
Inside, some 2,365 prisoners are either awaiting trial or serving time for some of the most serious of crimes: murder, abduction, trafficking, and armed robbery.
The prison’s director, Major Manwell, greets us at the front door – an almost three-metre tall gateway made of green steel. He is wearing a khaki safari suit and leather sandals.
“How can I help you?” he asks with a knowing smile.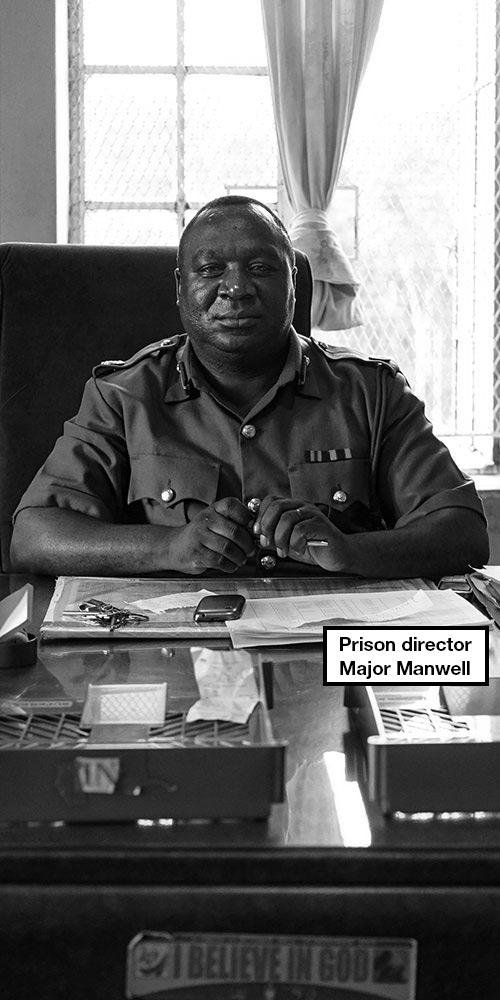
Manwell hands us over to two prison guards who lead us into an open corridor between the front desk and the staff kitchen. A makeshift clothes line hangs nearby. We sit on a bench, shaded by the prison’s towering walls.
Over the next three hours, we will meet eight prisoners who are either awaiting trial or have been convicted of playing some part in an attack on somebody with albinism.
One at a time, they sit opposite us on another wooden bench, a translator beside them.
A guard sits at a distance – far enough that his presence doesn’t feel intrusive, but close enough to eavesdrop. His body language tells us when he finds an inmate’s story of interest. When he doesn’t, he slumps back into his leather chair.
Just two of the inmates acknowledge that their case is related to someone with albinism. Most insist that they were framed or have been wrongly accused. Only one admits to having committed a crime.
“They are not able to come to terms with their crimes,” says the guard, removing his cap so that he can scratch his head. “They are in denial.”
The tomb raider
Stenala Shaibu Lizahapa is wearing a clean white shirt and tattered jeans. He takes his seat slowly and crosses his legs. A thin row of rosary beads pass through his fingers. Stenala is not in a hurry. Unlike the others, he doesn’t fidget. He simply sits and waits.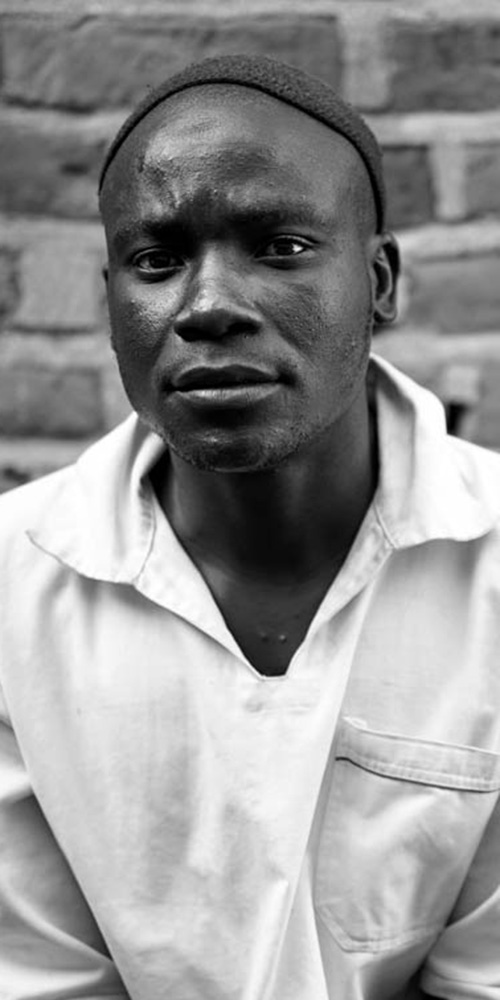
He is in his mid-30s and has been convicted of trespassing on a gravesite to remove three bones from the body of a deceased man named Awali Mandevu.
Along with five others, he was caught trying to sell the bones to an undercover police officer in April 2015.
All six were charged with criminal trespassing, removal of human tissue and selling human bones.
Three of them, including Stenala, pleaded guilty. Two others denied the charges and were acquitted, while the case against the sixth was dropped.
Stenala was sentenced to six years in prison.
He says he has made peace with his crime.
“What I did was wrong, but I felt desperate,” he says softly, only briefly making eye contact. “I feel ashamed.”
If there is a market [for bones], I don’t know… I would have believed it if I saw it. – Stenala Shaibu Lizahapa, sentenced to six years in prison for selling human bones
As a fisherman, he says he was earning K500 (70 cents) a day. So when friends asked if he’d help them deliver a set of bones to a client – promising it would make him “rich enough to drive” – he says he was tempted.
“With my income, I can’t afford a motorcycle, but a car – that was a dream … The devil took over me,” he says.
In early April 2015, Stenala travelled with friends from Machinga to his home district of Jali, where he went to Chinangwa, a village neighbouring his own, in search of a grave he’d been told housed the corpse of a person with albinism.
“Who doesn’t want more money?” he asks rhetorically. “I knew it was wrong, but I did it for my family.”
“If there is a market [for bones], I don’t know,” he says. “I would have believed it if I saw it.”
The victim’s family
Chinangwa village, Zomba district, southern Malawi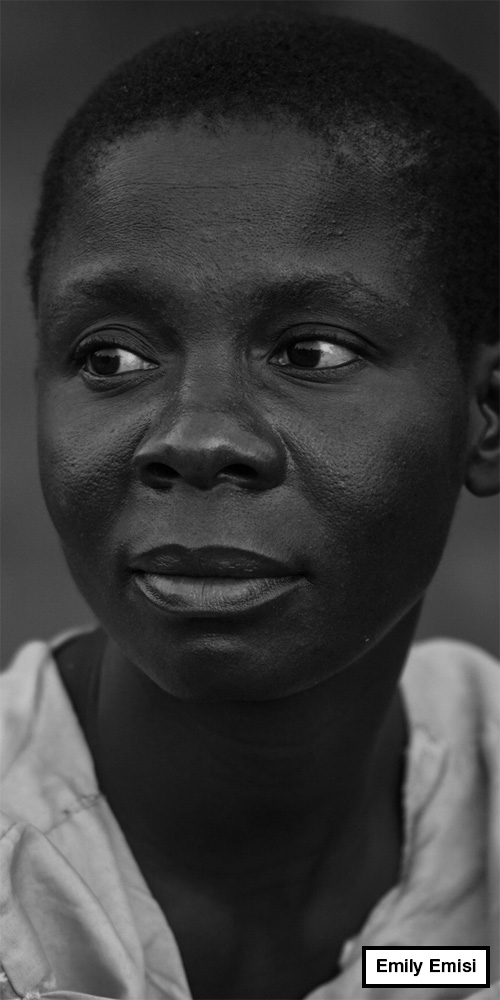
In the village of Chinangwa, Emily Emisi is sitting on a straw mat outside her mud brick and thatch-roofed home.
She offers us a mat on which to sit – between a couple of brown puppies and some corn drying in the winter sun.
“Why didn’t you call before you came?” the 36-year-old asks with a smile. “I would have cooked.”
Her generosity betrays her means. Her open yard – like the barren plateau that surrounds it – is hard brown earth. A few mango and small kachere trees surround the settlement.
Three children sit on the floor. For a while, they watch curiously. But when the novelty of strangers wears off, they return to kicking a punctured miniature football.
“It was my grandfather’s grave that Stenala dug up,” Emily says. “It was terrible. He was buried a long time [ago], in the 1990s. And this felt like a second funeral for him.”
Emily says it didn’t come as a surprise to many of the villagers when they learned that Stenala was responsible.
“He was known to steal goats,” she says.
Stenala had got into an argument with his brother weeks before when he’d tried to persuade him to help find the bones, Emily explains. His brother had refused and the argument had turned into a fight. The whole village heard about it, she says.
“Then, he tried to romance an albino girl, but the girl refused and told villagers that she was being pursued by him.”
She is “happy he has been put away”, she says, because he would “terrorise the village”.
Someone close to Stenala must have betrayed him, Emily speculates, because nobody knew that the village graveyard had been tampered with.
But, while she has no doubt that Stenala had been searching for the bones of somebody with albinism, Emily says he dug up the wrong grave.
“My grandfather, Awali Madenvu, was not an albino. But his grave was close to an albino and so they got the wrong bones.”
That wouldn’t have made any difference anyway – the penalty in Malawi is the same.
Because his was not a case of murder or attempted murder, Stenala wasn’t eligible for legal aid and so had no representation in court.
He was tried, sentenced and given 30 days to appeal.
When we tell Emily that Stenala admits his guilt and is remorseful, she clicks her tongue and looks away. “Of course, after the hardship in jail, he is going to be remorseful,” she says.
“He is not someone who will change. We all think that his sentence is too short, and we expect him to come back and teach us a lesson.”
‘I will wait for him’
As the sun is about to set, the silhouette of a woman appears through a haze of dust. She has a girl at her side and a baby in her arms.
“That is Annie Fuleya,” a young girl says. “Stenala’s wife.”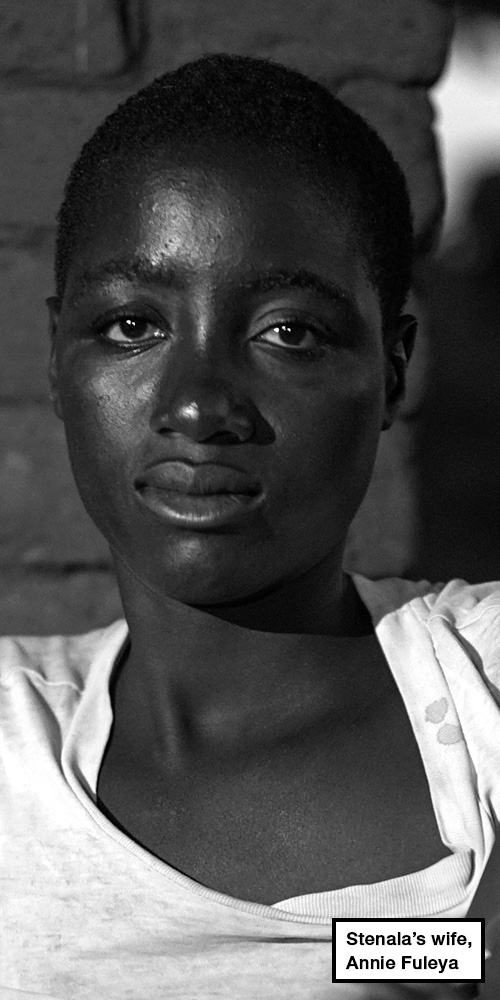
She is on her way to gather wood. Stenala’s home village of Jali is just a few hundred metres away. Emily’s family crosses paths with Stenala’s every day.
Annie is tall with a brush-cut. She wears a long green skirt and a pale blue T-shirt.
In the weeks leading up to the incident, the 26-year-old says her husband was acting strangely. She recalls asking him to stay away from a friend she thought was trouble.
“I didn’t believe it at first but then after the conviction I felt let down by him,” she reflects, looking away as she completes her sentence. Then, without looking back at us, she adds: “I believe that he did it.”
Annie was pregnant when her husband was arrested and must now raise their four-year-old daughter Saamyato and their now 14-month-old baby Latifa alone.
She left Machinga for Stenala’s village after his arrest, believing it was safer to be close to her mother-in-law. Now, she works in other people’s fields and depends on financial support from the extended family to help raise her children.
“All I know is that he was found with body parts of an albino. I don’t know what parts. I don’t know what he did. I just feel disappointed,” Annie says, holding on to Latifa as the baby wriggles in her arms.
“But I understand that he may have done it because of our situation. He doesn’t earn enough as a fisherman. He looks after me, his mother, my mother, and two orphaned children from an aunt,” she explains softly. “Perhaps this is what drove him to do this.”
“I will wait for him. Because I have forgiven him,” she adds. “But he will have to conduct himself properly on his return.”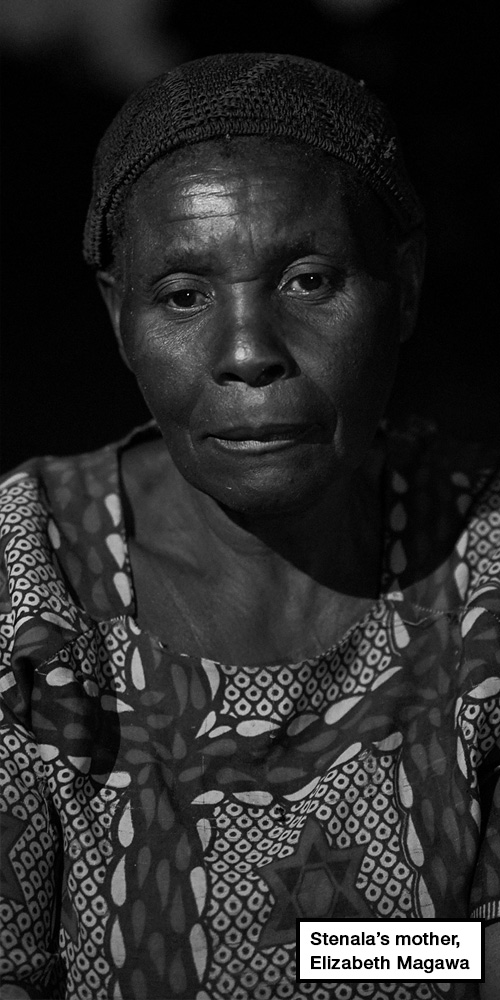
Stenala’s mother, who has been watching pensively as her daughter-in-law talks, agrees to speak to us under the shadow of a large kachere tree. Elizabeth Magawa is 49, and the resemblance to her son is immediately apparent. She smiles when we tell her this and the children who have gathered around, burst into laughter.
Elizabeth seems tired. She says she has aged over the past year.
“I didn’t look like this,” she sighs. “I spend sleepless nights wondering why Stenala would have done such a thing. He always helped the family.”
“It is something I will never understand,” she says. Then, she adds: “But I know he was fully capable of such a thing.”
Maybe Stenala did it because of our poverty, or because of peer pressure. I don’t know. – Elizabeth Magawa, mother of Stenala Shaibu, sentenced to six years for selling human bones
Her son’s arrest brought the family unwanted attention in the village, but Elizabeth says they haven’t suffered any serious repercussions.
“There was a lot of talk. They spoke about bones. But they’ve moved on,” she says.
“Maybe Stenala did it because of our poverty, or because of peer pressure. I don’t know.”
It has grown cold now and, without warning, Annie stands up and walks away, in the direction of her mother-in-law’s house.
Elizabeth watches as her daughter-in-law disappears into the darkness, her young daughter in tow.
Charles Nyasa: Convicted of trying to sell human tissue
Charles Nyasa cries as he tells his story.
The 24-year-old from Zomba district was sentenced to six years for being in possession of human flesh in March 2015.
He says he heard an advert for a witch doctor on radio or television – he can’t recall which – that promised “quick riches”. But when he visited the witch doctor, he was told to bring the placenta of a newborn. So, he says, he spent K8,000 ($11) buying one from nurses at a hospital.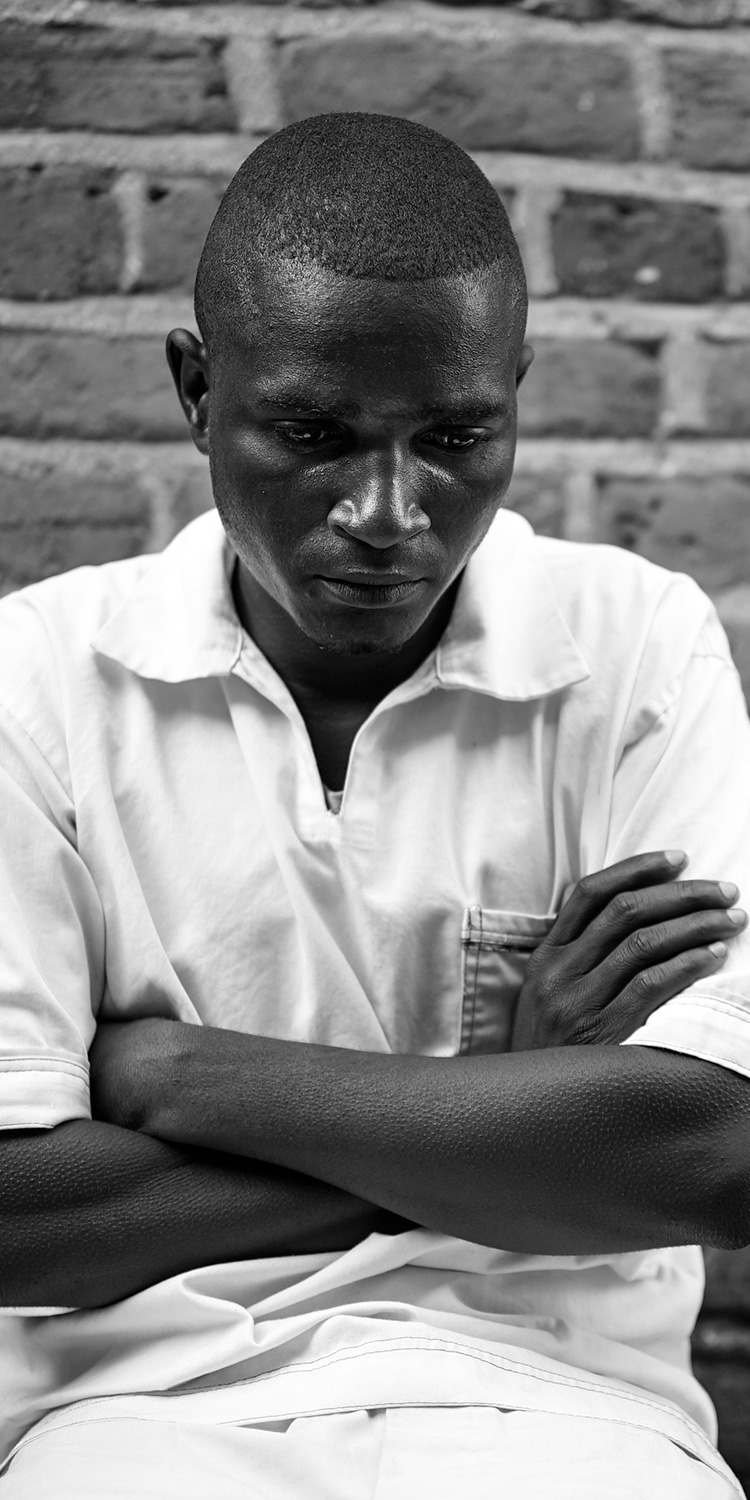
When he took it to the witch doctor, he was accused of carrying a placenta from a newborn with albinism.
He was convicted but insists his case had nothing to do with albinism.
John Alfred: Convicted of trying to sell a child
Thirty-one-year-old John Alfred looks older than his years. He is feverish and sweating profusely, but wants to talk.
John was sentenced to six years in prison for trying to sell his own child.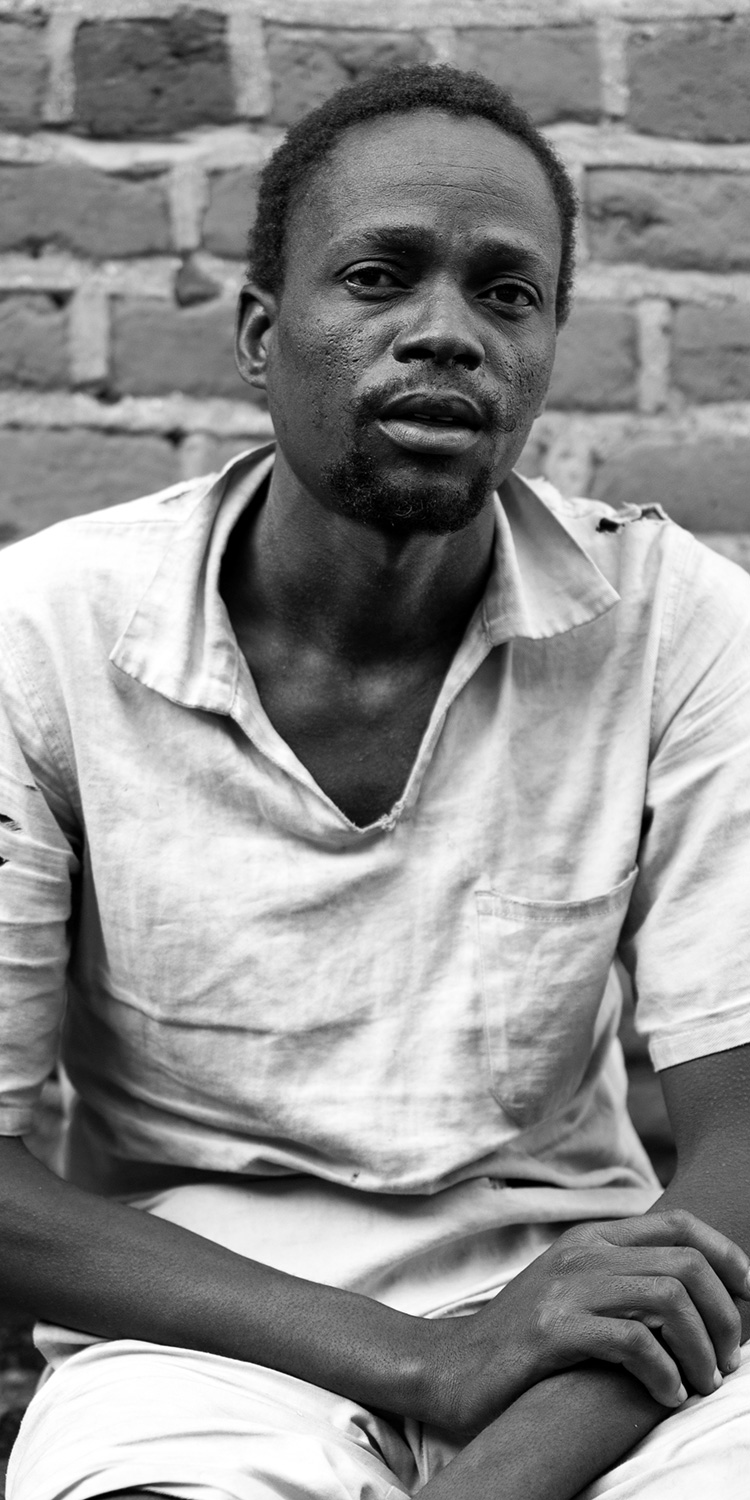
“I did it because of my [financial] condition. No other reason,” he says, shaking.
The father of five from Naweta village, in Machinga district, was earning K4,000 ($5.50) for two weeks’ work in the gardens and on the farms of a businessman.
“My boss saw me living in poverty and said to me one day: ‘Why don’t you be brave, and sell that child of yours?’ pointing to my daughter Vanessa. He said there were buyers in Mozambique for children like her.”
I had five children, and I thought that maybe it wasn’t a problem to get rid of one.– John Alfred, sentenced to six years for trying to sell his daughter
John says that his daughter does not have albinism but “resembled one”. The authorities at the prison say the child does have the condition, although there is no mention of it in his prison file.
“I had five children, and I thought that maybe it wasn’t a problem to get rid of one,” John says.
In April 2015, without consulting his wife, he took their four-year-old daughter and left for Mozambique.
“I didn’t know where I was going. I was just going to Mozambique to find this market,” he says.
But the police intercepted him in Machinga and arrested him.
“I admitted it in court and was sentenced,” he tells us.
Melinda Mbendera: Convicted of attempted kidnapping
Twenty-year-old Melinda Mbendera is agitated. She twitches and bites her lips as she talks.
She was found guilty of trying to kidnap a child with albinism and sentenced to three years’ imprisonment. But she insists that she is innocent. The court didn’t have enough evidence, she declares, and based their verdict solely on the claims of the child and her parents.
She says the judge told her that it would be safer for her to be in jail than on the streets, where she might face mob justice.
In 2016, 11 people suspected of being involved in digging graves or carrying human flesh were lynched in Malawi. In one case in the Nsanje district in March 2016, seven witch doctors accused of using bones in their potions were burned alive. A month earlier, a courthouse in the South Lunzu township in Blantyre, was razed to the ground after three people accused of murdering somebody with albinism had been bailed.
Melinda says she previously spent eight months in prison for stealing K200,000 ($275) from a family friend. She suspects her criminal record influenced the verdict in this case.
But, she maintains: “I didn’t spend eight months in this wretched place only to go out and commit another crime.”
“The police said that because I stole before, the probability was high that I did this … but why would I sell a human being?” she asks.

4 – A Question of Justice
Zomba, southern Malawi

Edge Kanyongolo is a tall man with thick eyebrows and an even thicker moustache.
The associate professor of law at the University of Malawi in Zomba is sitting behind his desk. Behind him, a window showcases a courtyard garden. Beside him, textbooks and legal reports are carefully stacked on a wooden bookshelf.
“The attacks on persons with albinism are a manifestation of a larger problem,” he says. “On the surface, there is the question of superstition and witchcraft, but I think underlying all of that is desperation.”
Malawi has been in an economic crisis since 2012. It began when tobacco, the country’s premier export, dropped in price by more than 50 percent in 2010. In 2012, under the guidance of the International Monetary Fund, President Joyce Banda imposed a range of hard-hitting economic reforms that were most harshly felt by the poor. The currency was devalued by almost 50 percent and inflation reached more than 20 percent.
In 2015, the World Bank rated Malawi as the poorest country in the world, per capita.
Two out of every five Malawians of employable age are without work. According to the International Labour Organisation, three in four young workers have only irregular employment, while nine out of 10 work in the informal sector, where their employment is precarious and may change daily. At least 61 percent of Malawians live on less than $1.25 a day and 2.3 million are said to be food-insecure.
“People don’t have options to earn money. And this then drives them to be so desperate and, as some would say – so irrational – as to think that getting the body parts of a type of person and so on, may make you rich,” the professor explains.
But Elijah Kachikuwo, the senior deputy commissioner of police in Mangochi, disagrees. In fact, he grows agitated when questioned about the connection. He is standing in the dusty courtyard of the main police station in Mangochi.
“It is not poverty that is causing this,” he declares, the lines on his forehead deepening. “We aren’t faced with poverty for the first time in the country. We shouldn’t hide behind this … so that question is out of order.”
The traditional healers
Mphalare in Dedza, central region of Malawi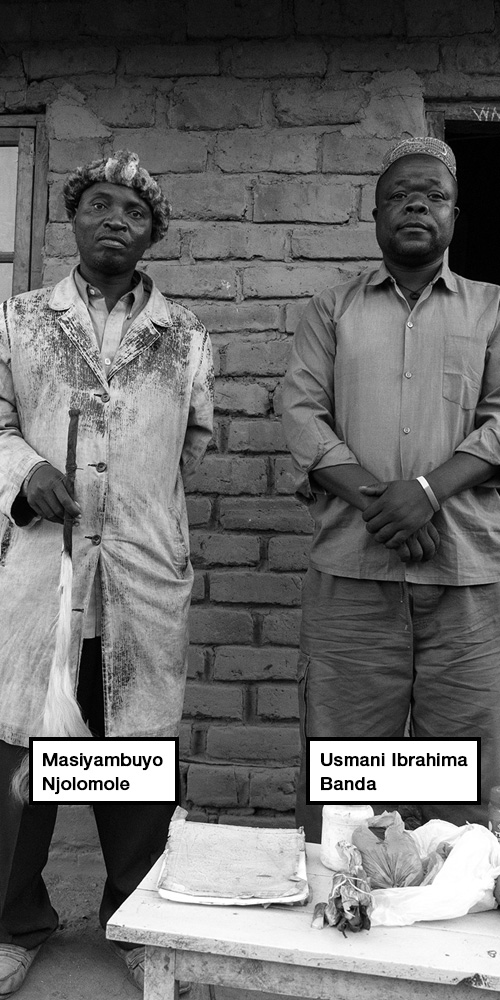
Masiyambuyo Njolomole and Usmani Ibrahima Banda live in the remote village of Mphalare in Dedza. It is 80km – about an hour’s drive along a dirt track – from Lilongwe.
They are both traditional healers.
Seven wooden stools lined up against a wall and a small coffee table are the only furniture inside the house where we meet them. There is no electricity, so the door has been left ajar. The sunlight illuminates the two men’s faces. A woman sweeps the yard outside, scraping at the dry earth.
Usmani wears a skull cap; Masiyambuyo a headdress made from monkey skin. The latter smiles as he presents his registration card. Usmani’s expired in 2011.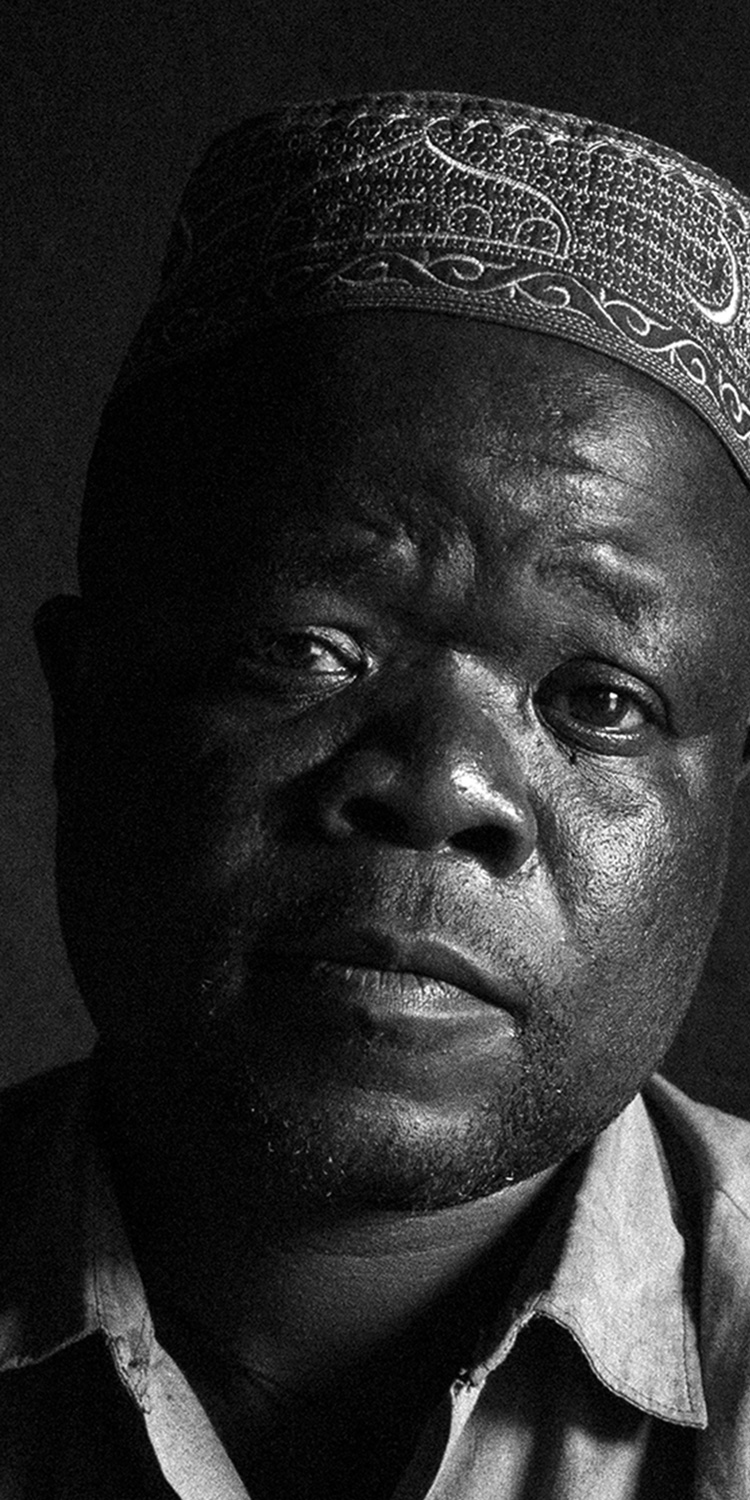
Masiyambuyo, a tall, thin man, makes it clear that neither of them use bones of any kind in their potions. He says “people like him” are being made scapegoats for criminals and a political conspiracy because the government has lost control of the situation. “This is a syndicate by some influential people in this country who are interested in body parts of albinos. They simply want to take the attention away from them; that is why they are accusing us,” he declares.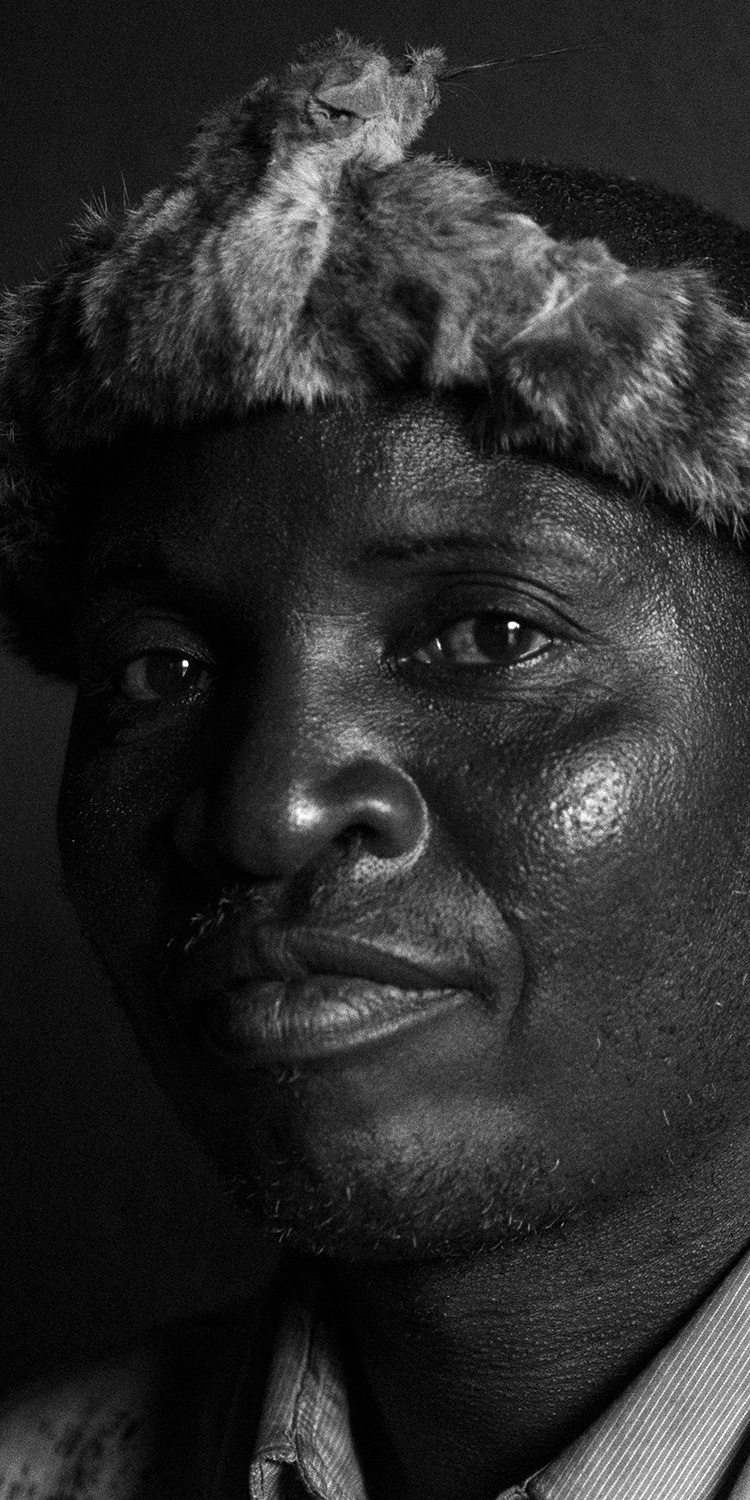
“Albinos have existed for a long time and we have also existed for a long time,” he adds.
In June 2016, Malawi’s High Court banned “witch doctors, traditional healers, charm sellers, fortune tellers and magicians,” in an effort to quell the trade in the bones of people with albinism.
Traditional healers such as Usmani and Masiyambuyo argue that only hurts the people they help.
“People think we deal with witchcraft, but we are here to help people,” Masiyambuyo says, earnestly, opening his arms.
According to the Traditional Healers Association of Malawi, up to 97 percent of the population visit traditional healers and herbalists. It is hard to verify this but it is clear that many people do use them, particularly in rural areas, where the state is often conspicuous by its absence.
There are two physicians and 59 nurses for every 100,000 people in Malawi. The ratio is the lowest in all of sub-Saharan Africa
Usmani says that, in such circumstances, the services he and Masiyambuyo provide are critical.
People think we deal with witchcraft, but we are here to help people.– Masiyambuyo Njolomole, a traditional healer based in Dedza
He was trained by his father, the softly spoken traditional healer explains, and used to specialise in sexually transmitted diseases. But, “nowadays, [it’s] cancer, blood pressure, asthma, using herbs and a mixture from seven trees” he adds, showing us plastic packets of concoctions made primarily from plants.
“People come to me when the hospitals have failed them.”
Dr Chilani is the spokesperson for Malawi’s Traditional Healers Association and tells us over the phone that “everyone [in the country], [from] farmers to politicians” uses traditional healers.
Many believe that illness involves an “element of being bewitched”, he explains. But, he insists, “sending people to kill others” isn’t part of their craft.
“We help people, we don’t kill them,” he says.
The new law targeting unlicensed traditional healers would purportedly help end these crimes. But the line between traditional healer and witch doctor isn’t always clear.
Mary Shawa, the former principal secretary at the Ministry of Gender, Children, Disability and Social Welfare, says the distinction lies in registration. “No one who obeys the law needs to feel threatened,” she explains.
Chilani’s Facebook page offers “revenge spells, fertility spells, magic rings and witchcraft spells”, but also asks that anyone with information about the bones of somebody with albinism contact him so that it can be reported to the police. He says no one has been in touch.
“If we have been around for generations, and the killings of persons with albinism began roughly two years ago, what were we doing all this time?” he asks.
One lawyer for every 38,500 Malawians
Lilongwe, central region of Malawi
Piles of paper cover Masauko Chamkakala’s desk. The director of Legal Aid, the body tasked with representing those who cannot afford legal representation, is in his office in Area 4 of Lilongwe.
The country’s legal system, he says, is a mess.
“More than 90 percent of the population cannot afford legal representation. We have seven lawyers for the entire country,” he says, his hands clasped and eyebrows raised.
The Legal Aid Act stipulates that anyone charged with a crime that could result in a custodial sentence is entitled to legal aid, but limited resources have resulted in the courts restricting this to homicide cases.
A 2013 report found that Malawi had fewer than 400 lawyers. That was one lawyer for every 38,500 people.
The jails are overcrowded and suspects can wait months or even years before their cases go to trial.
“If you go to the prisons [and] start going through the cases, you realise that so many of these people are not supposed to be there,” Masauko says, pointing out that: “For an ordinary person to get an appointment with a lawyer will cost him K20,000 ($27), while the [monthly] minimum wage is K18,000 ($25).”
Then there is the question of entrapment – a method that police officers have admitted to using but one which has so far led only to the arrest of sellers.
More than 90 percent of the population cannot afford legal representation. We have seven lawyers for the entire country.– Masauko Chamkakala, the director of Legal Aid
In a side office near Malawi’s High Court, Neverson Chisiza, a senior state advocate at Malawi’s Ministry of Justice and Constitutional Affairs, acknowledges that there have been discussions within the ministry about “why it is always sellers, those who are desperate [and] looking for quick money, [who] are caught, not the buyers”.
And without the buyers, the police are little closer to understanding the source of this trade.
Masouko says that the hysteria over the killings of people with albinism has reached such a height that “it is possible a person could be convicted for carrying antelope bones because they resemble human bones”.
And, he adds, those accused of any crime related to people with albinism are tried in “people’s courts”.
A question of government preparedness
Lilongwe, central region of Malawi
It is late on a Friday afternoon when Mary Shawa meets us in her office and her team are about to leave for the day. She is responsible for the security, health and wellbeing of Malawians with albinism.
“Until the atrocities started, we didn’t look at persons with albinism as people with a disability. We saw them as ordinary people,” she says, adjusting her glasses.
She slumps back into her chair. “If you look at the demographics, they are young and old, some working as lawyers and teachers, some still in school,” she adds.
Before moving to this ministry in 2012, Mary was the secretary for nutrition, HIV and Aids in the president’s office, credited with tackling the country’s HIV pandemic.
She speaks authoritatively and frankly, rejecting any suggestion that the government hasn’t done enough to address the crimes committed against people with albinism. She rattles off the details of cases that have been solved and cites “ministerial research” to suggest that there is no market for the bones.
“[The] culprits get the bones and walk around looking for a market to sell them,” she says.
Mary says her ministry has been leading a communications plan to tackle the crisis. “The radio messages, the billboards, this is all us,” she explains.
But it’s hard to tell if anyone is listening.
“We are also compiling a census, to register all persons with albinism in the country,” she says, leaning forward, her hands resting on the desk.
But beyond the issue of security, people with albinism have other needs – sunscreen, hats and sunglasses to protect them from the sun. The Ministry of Health does provide zinc oxide at clinics but that only helps with the blisters and lesions and doesn’t offer any protection. Moreover, patients have to travel to the main cities to access the ointment.
Mary hints at a lack of funding. Malawi is heavily reliant on donors, and it’s unlikely that sunscreen or hats top the government’s financial priorities or a foreign government’s agenda.
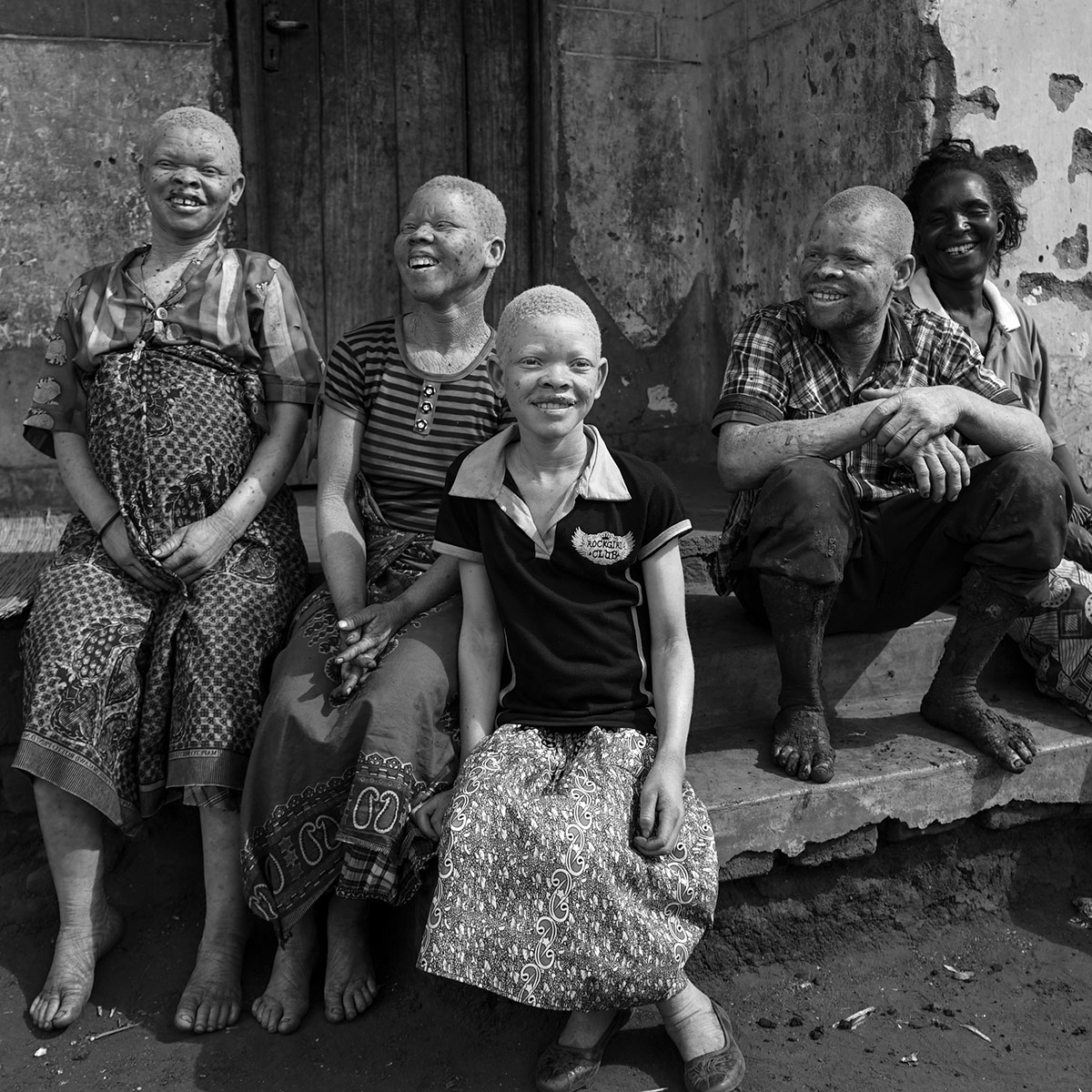

Village of Nambilikira, Dedza district, eastern Malawi
5 – The Future
Confident, assertive and friendly, Clement Gweza seems as though he was born to teach. He transforms the 60 rowdy teenagers into an orderly classroom and begins his social and environmental science lesson by scribbling “How to prevent air pollution” on the blackboard.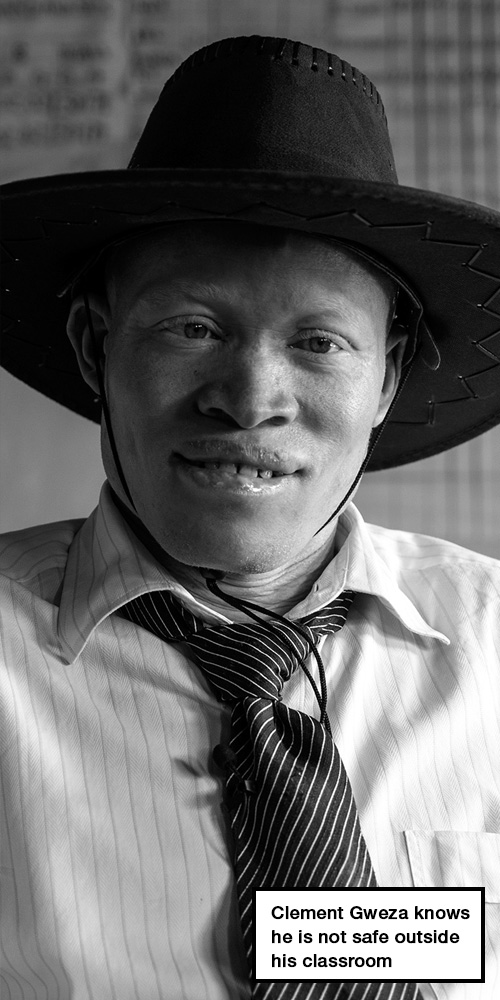
The 24-year-old is smartly dressed in an off-white shirt, pinstriped tie and black trousers.
“It was difficult at first,” he says. “The children found it hard to understand my albinism, because people, not just the learners, don’t think that a person with albinism can do something that can be recognised by society.”
He became a teacher, he says, because the tuition was free and he couldn’t afford to pay to study anything else.
At first, he worried that his students wouldn’t respect him. But, he says, “after a few weeks, the learners came round. They will tell you: ‘Ah! He is a good teacher and he understands our problems’.”
But he knows that, despite the respect he enjoys in the classroom, he is not safe outside of it.
The murder of one of his students, David Fletcher, made him afraid.
He has stopped walking outside at night and, if he must, he asks a close friend or relative to accompany him.
“If I can’t find someone to take me home, I will stay where I am and sleep there. I have no choice,” he says.
“Everything has changed. I look at the people, the friends around me, and I think ‘maybe he wants to kill me and make some money’.”
Stercia Kanyowa’s story
Masumpankhunda, in Lilongwe, central Malawi

Twelve-year-old Stercia Kanyowa says she doesn’t want to beg. She wants an education, and to stand on her own two feet.
“I want to be a teacher first. Then maybe a journalist or a bank manager,” she declares.
Stercia is one of three children with albinism at the Malingunde School for the Visually Impaired. As an only child from a single-parent household, she says completing school is her only hope for the future. She has been here since 2011.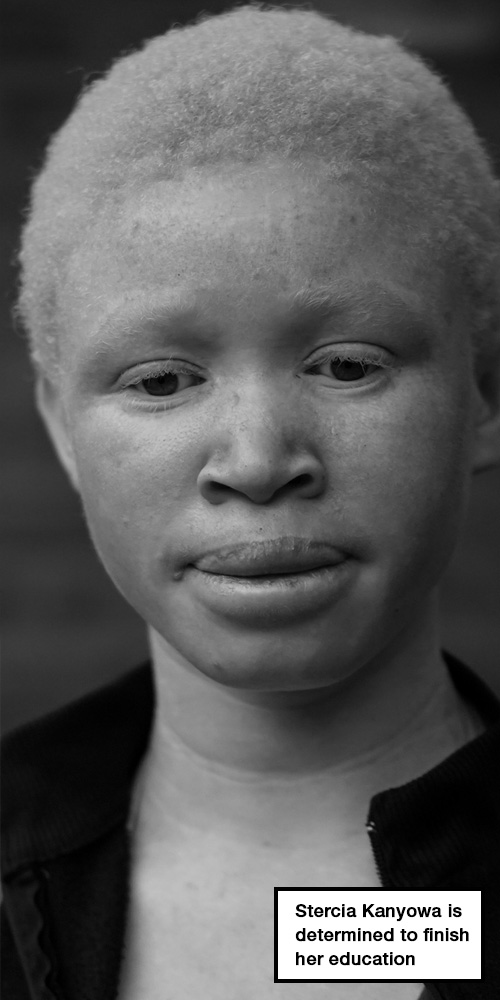
“Of course, I miss home. It’s long since I have gone home. Who doesn’t miss home?” she says, outside her dormitory.
The school is government-run, and functions almost exclusively on donations. There are 17 classrooms and 40 teachers for 3,000 students.
There is no electricity. Inside Stercia’s classroom, some students are huddled around braille machines, while others, such as 15-year-old Foster Kennedy, who also has albinism, use a magnifying glass to read textbooks.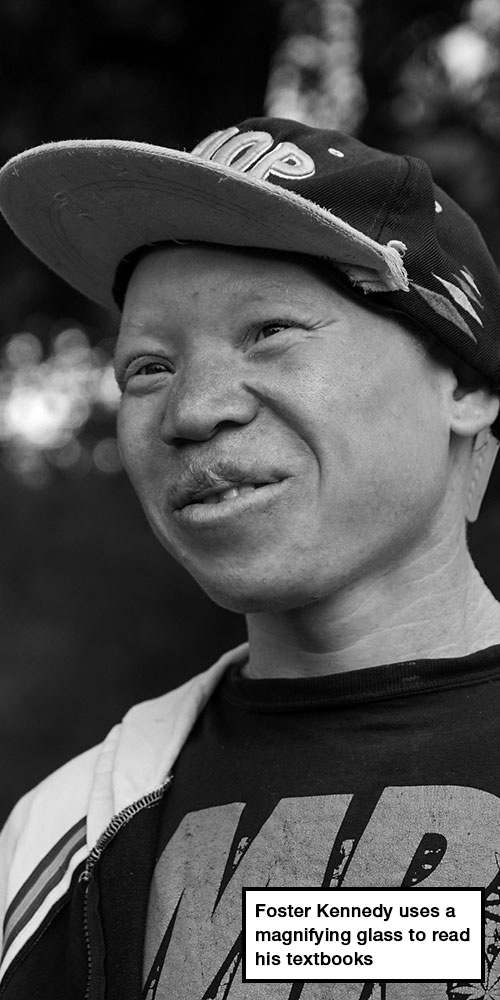
“Everyone here is a friend. You would think we are born from the same mother,” Foster says, smiling.
He wants to be a radio personality or a songwriter, he explains.
The school yard is a thoroughfare for people walking or cycling to the town centre, which means that there are always strangers passing through. This concerns the school authorities. Without a wall or a gate, the school is vulnerable to theft and the students to being attacked. In early 2015, a 16-year-old student with albinism was almost abducted by a stranger who promised to buy her supplies from the local market.
“It is an open place. And anything can happen,” says Chiko Kamphandira, the school principal.
Back outside, Stercia, who is head of the school choir, begins to sing one of her favourite songs, before stopping suddenly, self-conscious and shy.
“I am going to work hard and fulfill my dreams,” she says. “I don’t see myself as any different. I am just a human being.”
Ian Simbota’s story
Blantyre, southern Malawi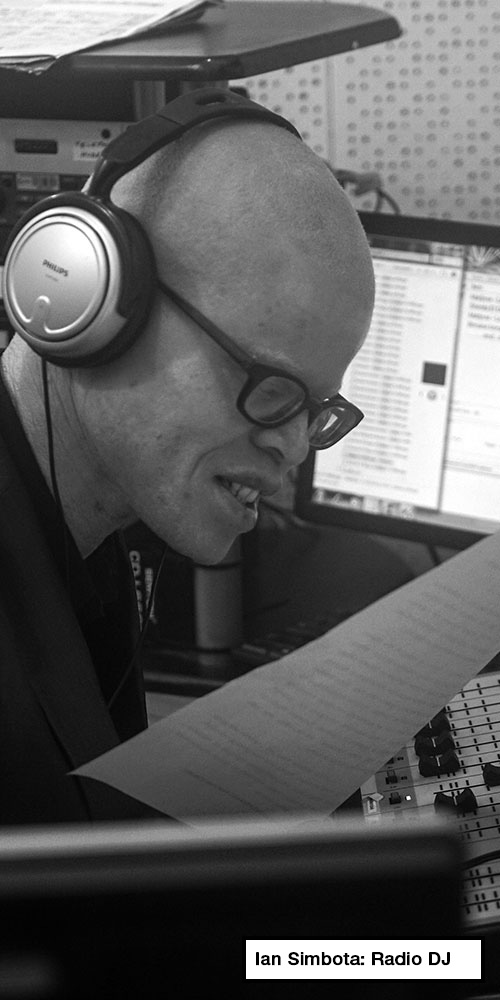
Ian Simbota is eating a chicken tikka burger at a Pakistani fast food diner when we spot him one evening in Blantyre.
When we ask to talk to him, he scans our journalists’ credentials before agreeing. It turns out that he gets paid to talk as a late-night radio talk show host and a DJ with the Malawi Broadcasting Corporation. And he has just returned from Kasungu, in the central region of Malawi, where he was the master of ceremonies for World International Albinism Awareness Day.
When he finishes his meal, he invites us to the radio studio.
Once on the airwaves, the slightly pensive man we met at the restaurant is no more. He taunts and teases his listeners. The studio is his safe place.
Later on, he talks of a double life. As a radio star, his voice and name are widely recognised. But not all of his listeners know that he has albinism. And there are times when his confident persona gives way to fear.
“Look, I am working at night. And people know I am here,” he says. “What are they thinking, planning? From here I will get a car and go home. And when I go home, I feel unsafe. What if they attack me? I think about it all the time.”
Ian became a full-time DJ in 2015. It was a dream come true. “I wanted to be a midwife as a child [but] thankfully my mother convinced me otherwise,” he laughs.
“And then, I wanted to be a radio host. Geoffrey Zigoma [the gospel singer] made a huge impact on my life.”
But life hasn’t been easy for Ian.
When he was born, he was the second child in his family to have albinism. His father walked out on them.
“My father told my mum to kill us. When she refused, he left,” he says, matter-of-factly.
“At that time, people didn’t know about the genes and stuff. My dad thought it was a curse.”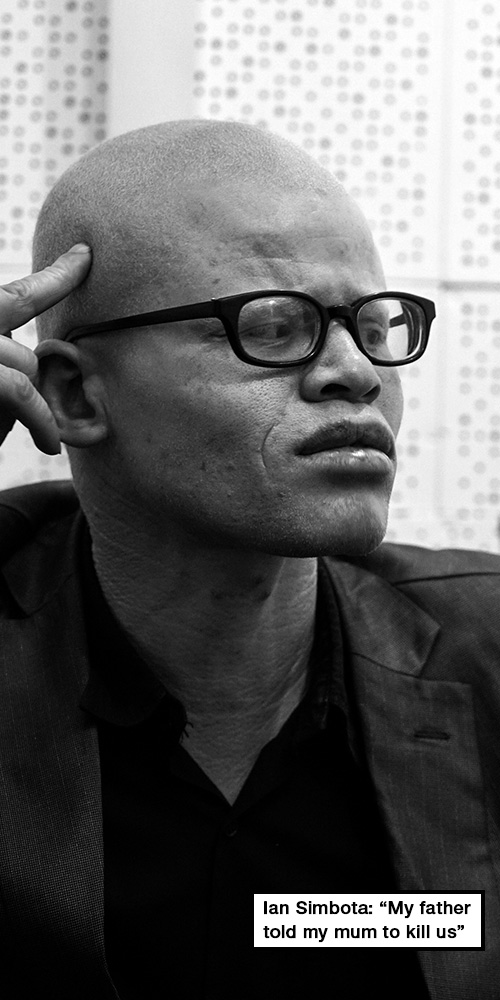
Ian’s mother left her village in southern Malawi and came to Blantyre with her two children to look for a job. She found one as a cleaner at the College of Medicine.
His father remarried. His next child was also born with albinism.
School was tough for Ian. He says his teachers didn’t realise that he was visually impaired so would just call him lazy. When he completed his certificate in journalism and applied for internships in radio, his visual impairments worked against him again – station managers were concerned that he wouldn’t be able to see the computer screens, he says.
Then his mother died after a prolonged illness, and the new job felt like the start of a new life for him. But then the attacks on people with albinism began.
“I can tell you, it has become difficult,” he says. “I have friends. But at this point in time, I only trust one friend in my circle. I have other friends, but then sometimes, you just wonder, you know, maybe, he is being used [to get close to me].”
He also has to face harassment on the streets and says his girlfriend left him last year because “she couldn’t deal with what … [he] was going through”.
But today he’s the voice of a successful radio show.
“I like radio because you could come naked to the studio and it doesn’t matter. People are listening to your voice,” he says, pausing for a second, before laughing.
“I have done a little bit of TV, but radio is better because listeners create a different picture of what they think you are. It’s only now [with the crisis] that people realise I am a person with albinism …”
Source: Malawi: killed for their bones – on the trail of the trade in human body parts