I have written extensively about Liberia’s history of ritual killings, in books, articles, and on my website ‘Liberia: Past and Present of Africa’s Oldest Republic‘, notably in the section ‘Past and Present of Ritual Killings: From Cultural Phenomenon to Political Instrument‘.
I was confronted with the phenomenon of ritualistic murders in Liberia when living in Monrovia – where I taught at the University of Liberia – and, later, in Harper, capital of Maryland County, in the second half of the 1970s. In Harper I witnessed the public execution of the Harper Seven, in 1979. They were convicted of the ritual murder of a fisherman and popular singer, Moses Tweh, and sentenced to death by hanging. The trial of the Harper Seven turned out to be Liberia’s most notorious ritual killing case.
‘Big shots’ were involved, such as Maryland County’s Superintendent, Daniel Anderson – son of the Chairman of Liberia’s only political party, the True Whig Party – and Allen Yancy, member of the House of Representatives for Maryland County and cousin of former Liberian president William Tubman (1944 – 1971). Reportedly, Allen Yancy had been involved in previous ritual murder cases but he was never convicted, allegedly because of Tubman’s protection.
Ritualistic killings in Liberia have been rampant, and I fear the gruesome practice has far from disappeared – as is demonstrated by the article reproduced below.
The article reproduced below summarizes well Liberia’s recent history of ritualistic murders. What used to be a cultural phenomenon – human sacrifices for the well-being of the clan or tribe – has become a political instrument, used by unscrupulous politicians and businessmen to further their interests.
I will not dwell too long here on these atrocities and outdated but persistent beliefs in supernatural powers. Readers are invited to visit my website for more details.
Last but not least, my publications on ritual murders in Liberia became the prelude to the present website on ritual killings in Africa in general. See the site’s menu, notably the section ‘Why publish this site?‘
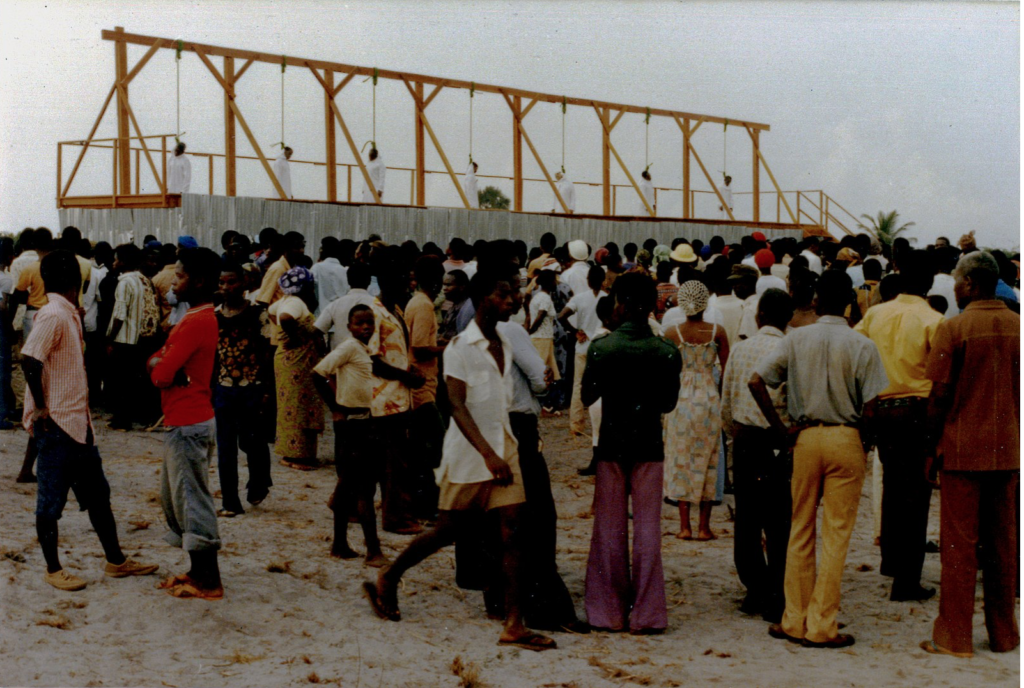

Public execution by hanging of the ‘Harper Seven’, including Maryland Superintendent Daniel Anderson and Representative Allen Yancy, at dawn in Harper, Liberia on February 16, 1979. Picture taken by Fred van der Kraaij (copyrights).
Liberia’s elections, ritual killings and cannibalism
Published: August 01, 2011 · 10:52 AM UTC
By: Emily Schmall and Wade Williams
MONROVIA, Liberia — The pregnant woman was found dead in the shallows of Lake Shepherd. The fetus had been removed.
A candidate for Liberia’s Senate and a former county attorney are among those standing trial for the 2009 murder, the latest in a long history of ritual sacrifices performed for political power in Liberia.
In this case in southeastern Maryland County, prosecutors were tipped off by a witch doctor who provided a list of 18 people allegedly connected to the killing, including Fulton Yancy, the former county attorney, and President Ellen Johnson Sirleaf’s Special Envoy and Ambassador-at-Large Dan Morias.
Vials of blood were discovered in Yancy’s home. Nine were charged with murder but were released earlier this month following a Supreme Court ruling.
Liberia will have general elections later this year and the ritual killings tend to flare up during election season, according to Jerome Verdier, former chairman of Liberia’s Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC).
”Unfortunately it happens during elections time because people are competing for political power, they don’t know God and they believe that these supernatural powers will come to them once human blood is shed,” Verdier said.
During Liberia’s two-decades-long civil war hundreds were killed for ritual purposes, the TRC discovered during its hearings.
”During our research at the TRC we found out that bloodshedding was very, very common during the conflict. People killed indiscriminately women and children believing that it would give them some power to continue fighting and that they would be protected,” said Verdier.
Liberia’s Maryland County has traditionally been the hub for the country’s ritual murders. The killings have haunted the southeastern county for decades. In recent years, however, ritual killing cases have cropped up across the country.
Verdier said some of those who confessed at the TRC hearing gave graphic accounts of ritual killings they carried out.
“People went as far as eating their opponent’s body — when such person is killed in battle they cook their body to eat, believing that the spirit, the powerful spirit of that person, will come to them and by eating them, the person’s power is completely destroyed, so there can be no reemergence in that person’s family line or their ethnic line.”

‘General Butt Naked’, a notorious warlord in Liberia’s First Civil war (1989 – 1997) testified and confessed before the Truth and Reconciliation Commission that he committed numerous ritualistic murders and ate body parts of his victims.
A former warlord who calls himself General Butt Naked and who fought against former Liberian dictator Charles Taylor, confessed in 2008 to taking part in human sacrifices that included the killing of a child and “plucking out the heart, which was divided into pieces for us to eat.”
In 2005, the leader of Liberia’s transitional government, Gyude Bryant, pledged to hang anyone found guilt of ritual killing.
Dispatched to Maryland County by President Johnson Sirleaf to calm residents’ fears earlier this year, Justice Minister Christiana Tah acknowledged that “there are still lots of unresolved cases of this nature,” according to a report in the daily New Democrat.
In a case from the 1970s known as the Maryland Murders, seven people, including Fulton Yancy’s older brother Allen Yancy, a member of the House of Representatives, were hanged for killing a fisherman (see picture above). The following year Defense Minister Gray D. Allison was convicted of killing a police officer whose body was discovered on the Bong Mines railroad, apparently used in a ritual sacrifice. The government at the time displayed blood drained in gallons believed to be that of the dead man.
Dan Morias, one of those accused of the 2009 killing of a pregnant woman, is planning to run for senator in the upcoming legislative elections in October. He has maintained that the charges against him are politically motivated. He must be cleared of the charges to be eligible to run for office.
Morias is listed in the TRC report for alleged abuses committed while he served as Minister of Internal Affairs for the Charles Taylor regime. When reached by GlobalPost, Morias said he could not comment on the case as it would be “prejudicial,” but insisted that the evidence against him — namely the testimony of a witch doctor — was “weak.”
Earlier this year, President Johnson Sirleaf warned Maryland County citizens against seeking retribution for the killings with a traditional practice called “sassywood” or “trial by ordeal.”
The government insists that trial by ordeal is illegal and Johnson Sirleaf banned the practice in April 2007. Since then traditional leaders have been pleading with the government to allow them to practice the act which they believe is the only way justice can be served in cases like these.
“Sassywood” is the insertion of an accused person’s extremity into hot oil or the placing of a heated metal on a suspect’s body. If the suspect is burned then it is concluded that he or she is guilty but if there is no burn then the suspect is deemed innocent and set free. Those found guilty are killed.
The police are working to stamp out both the ritual killings and the “sassywood” practices, said George Bardue, spokesman for the Liberia National Police: “The police are doing everything possible to make sure that these things do not happen.”
Emily Schmall is a multimedia journalist now based in Monrovia, Liberia, where she serves as country director for New Narratives, a journalism mentorship project for women. Wade Williams is a New Narratives fellow and an editor at FrontPage Africa, Liberia’s most widely circulated newspaper.
Source: Liberia’s elections, ritual killings and cannibalism
GlobalPost