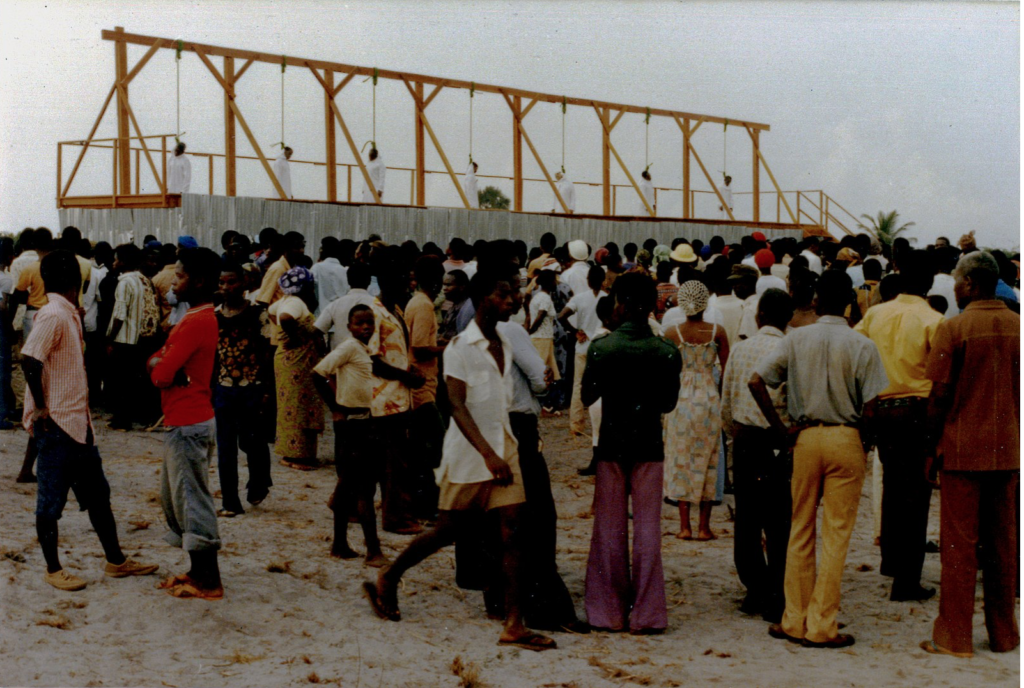
A former ULIMO commander stands trial in France accused of war crimes, human rights violations, murder and cannibalism.
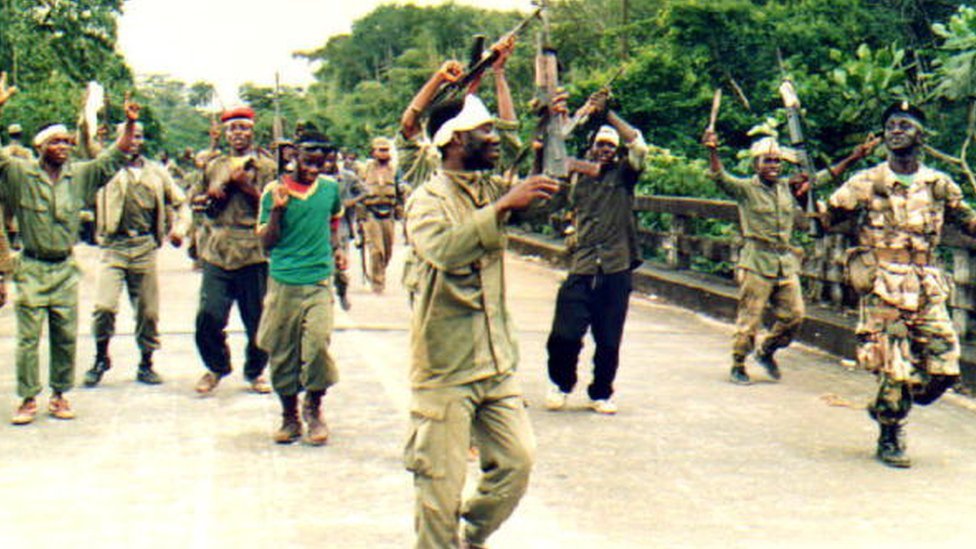

For shortness sake reference is made to Civitas Maxima’s monitoring of the arrest and trial of Kunti Kamara, a former ULIMO commander who was arrested in France in 2018. Kunti Kamara is accused of war crimes and human rights violations including torture, rape, murder and cannibalism committed during Liberia’s first civil war (1989-1997) in Foya, Lofa County, Liberia. His trial started in Paris/France on October 10.
Ritualistic activities including ritual murder and acts of cannibalism are well-known in Liberia. This site has reported frequently on ritual murder cases, the discovery of mutilated bodies, and unexplained disappearances which allegedly are linked to ritualistic activities. Election periods and the back-to-back civil wars (1989-1997; 1999-2003) are notorious peaks in the occurrence of ritual murders.
As far back as the 1970s, President William Tolbert (1971-1980) condemned ritualistic murders (‘An eye for an eye‘) and refused to grant clemency to seven convicted ritual murderers in what was perhaps Liberia’s most notorious ritual murder case (‘the Harper Seven‘). In 2005, the Head of the LNTG, Gyude Bryant, warned presidential candidates not to commit ritual murders to boost their chances. President Ellen Johnson Sirleaf (2006-2018) on more than one occasion spoke out against ritualistic murders. In 2017 people in Bong County protested against the ‘election year ritual killings’. More recently, during the Weah Administration (2018 – present), Liberia is again confronted with a wave of mysterious deaths, unexplained disappearances and ritual murders which has led politicians, religious leaders, civilians, to condemn these practices, urging President Weah to act.
Kunti Kamara is not the first or only rebel commander who’s being accused of ritual murder and cannibalism. The Truth and Reconciliation Commission mentions in its 2009 Final Report that hundreds of Liberians were murdered for ritual purposes during the two civil wars. In his book The Mask of Anarchy (1999), the late Stephen Ellis accuses the leader of the National Patriotic Front of Liberia (NPFL) who started Liberia’s first civil war, Charles Taylor, of drinking human blood during a juju ritual. Also Gibril Massaquoi, a RUF commander in neighboring Sierra Leone and a key-witness in the SCSL trial of warlord-turned-president Charles Taylor, was accused of murder for ritual purposes, but acquitted in April (2022).
(webmaster FVDK).
“I would never eat human heart” –
Kunti Kamara denies accusation before a French War Crimes court

Published: October 18, 2022
By: Prue Clarke, Front Page Africa – Monrovia, Liberia
PARIS, France – The former Ulimo commander Kunti Kamara, on trial here for war crimes and crimes against humanity in Liberia’s civil wars, had his first chance to make a substantive response to the allegations made against him in the first five days of this trial.
Under questioning from the judges, civilian lawyers and prosecution lawyers Kamara denied all the accusations that victims have made against him of torture, rape, murder of civilians and “barbarism” in the town of Foya in Lofa County, Liberia between 1993 and 1994.
Kamara told the nine-person jury and four alternates that the accusations of cannibalism – that he roasted and ate the heart of a civilian who had allegedly reported his crimes to international observers – made him sick.
“Since I was arrested nothing bothered me in the trial like what they’re talking about now. Eating human beings,” Kamara said. “Even if I spend 100 years in jail I will not admit to eating a human being’s heart. Each time I hear it I want to vomit.”
“Since I was born until today I never eat pork,” said Kamara a Muslim. “Why should I eat human being heart? I have nothing to say. I am innocent. I don’t know them today. I don’t know them tomorrow.”
Kamara denied that he had ever knew anyone who had said they ate human heart including in rituals of the Poro, a traditional African society.
“Since I was small that is a rumor in the ear,” he said of Poro human sacrifice and consumption of human flesh. “But I never met anyone who said they ate heart.”
Kamara insisted that the Ulimo committed no atrocities against civilians in the four-month period he was with them in Foya though he conceded Ulimo may have committed atrocities elsewhere during the war.
He said Ulimo in Foya was under the ultimate command of Ulimo Commander Dekau. Kamara said his mandate was only as battalion commander in charge of platoons “on the frontlines”. He denied any leadership role in the town over civilians.
Kamara acknowledged Ulimo fighters that victims have identified in this trial “Ugly Boy”, “Fine Boy” and Alieu Kosiah, convicted of war crimes in Switzerland in 2021, were all with him in Foya but Kamara claimed he hardly ever saw them.
Kamara blamed the accusations that have brought him to trial here were part of a “plot” orchestrated by “a clique” led by Fayah Williams, the late deputy director at Global Justice and Research Project, the Liberian justice activists.

Late in the evening Massa Washington, the former commissioner of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission, gave a powerful testimony that could prove decisive in the trial.
It was designed to answer questions that jurors may have had about whether they should be passing judgement on a Liberian for crimes committed 30 years ago in a country a long way away. That was a question French journalists were asking eachother on the sidelines of the trial.
“These trials are important because they give them people of Liberia justice,” an emotional Washington told the jury. “They give us hope that one day we’ll be able to get justice with our own judges, our own prosecutors, on our own soil. In the meantime we are grateful that some of the people who committed these gross violations of human rights who are in this country, in the US, in every country in the world where they find them they can try to bring them to justice. In the absence of our government addressing accountability these trials are the Liberian people have.”
Washington thanked the jury.
“It sends a message that we belong to the universal human race,” Washington said. “It says that the world has not forgotten Liberia. It says that we all share that common human dignity. We have the same needs. We feel the same pain. We thank you for the opportunity to tell some of these stories. I hope this has provided an important clarification for why this trial is important.”
Washington told some of the horrors she had personally witnessed as a journalist in Monrovia during the first civil war. The jury was riveted by her testimony which made clear that the testimony they were hearing from witnesses here was just a fraction of the myriad atrocities that had been committed during the war. She told of rapes of girls as young as five and of elderly women. She said her work with women made it clear to her than many of the elderly women had not come forward to the TRC hearings because of the stigma.
She told the story of an 82-year-old woman who told her she was made a war wife.
“’I was raped all the time by boys who could have been my grandchildren,’” Massa quoted the woman as saying. “Her story is just one story that represents thousands of stories. The rebels were so bad that when people were on checkpoints trying to get away from the fighting the rebels were raping the wives in front of the husbands. They even forced sons to have sex with mothers in front of the family to destroy the men. They took the young girls away.”
Earlier in the day the fifth victim to testify against Kamara detailed the alleged torture, killing and cannibalism of a schoolteacher in Foya that all victims have claimed was directed by the defendant.
He also talked more broadly of the suffering of people in Lofa during Ulimo’s occupation of the town. His telling of the experience of the women he had planned to marry was a harrowing example of the broader suffering of the people.
“M. was my girlfriend and Ugly Boy took her as a sex slave,” the victim told the Paris court talking of the now deceased perpetrator that many victims have alleged was Kamara’s lieutenant who followed his orders to commit many of the crimes. The court has ordered press to withhold victims’ names for their security.
“This was another blow to me,” the victim told the court. ”I really planned to marry her. The first time I saw her after the war, it was painful, but it had happened. She was not at fault. I saw her but the stigma was too heavy. I could no longer take her as a wife. By tradition anyone who takes a wife after that is easily rejected from society. In addition, because of her time as a sex slave, she conceived. I am feeling it for her now because her situation is too deplorable.”
The trial continues Tuesday with more testimonies from victims about the murder of a woman in Lofa.
This story is a collaboration with New Narratives as part of the West Africa Justice Reporting Project.
And:
Liberia: “You are Kundi. You killed my sister”
A third victim identifies Kamara as perpetrator in War Crimes Trial

Published: October 19, 2022
By: Anthony Stephens and Prue Clarke with New Narratives, Front Page Africa – Monrovia,
PARIS, France – On Tuesday a third victim identified Kunti Kamara, on trial for torture, cannibalism and crimes against humanity in the Paris Court, as “Co Kundi” the rebel commander who allegedly committed atrocities in Foya, Lofa County, Liberia.
The man was one of four plaintiffs who have brought the case against Kamara here in Paris, France where Kamara was living when he was arrested in 2019 after French investigators built a case against him.
“You are Kundi,” the man said turning to look at Kamara directly, barely containing his obvious emotion and rage. The plaintiff pointed at Kamara who was sitting behind his lawyers in a protective glass case. “I know you very well. You the one that killed my sister.”
The now elderly man told the court Kamara arrived at his house in Foya in late 1993 after the man’s sister’s baby had died. He alleged Kamara gave the family $L100 for their pain.
Soon after that Kamara allegedly ordered the victim’s sick and half naked sister – the mother of the child – dragged from the house. He accused her of witchcraft. The victim said Kamara and his troops had taken over the house for themselves and already had his wife, son and mother in custody at the time. Kamara did not know the man, who was standing with a crowd, was a member of the family.
The victim was overcome with tears as told the court that he had watched as Kamara put three bullets in his sister’s head.
Within months the man’s mother was also dead from illness. The victim blamed Kunti for the grief the murder of his sister had caused her.
“She cried every day,” he said. “So she became sick from not seeing my sister.”
The lawyer for the civil parties asked the victim if he had anything to say to Kamara but he took the opportunity to issue a warning to the judges instead.
“I’m very happy to see all the officers to take care of Kundi,” he said pointing to the court officers who accompany the defendant at all times. “This government should not leave Kundi to come back to Liberia.”
Kamara rejected all the allegations as he has done consistently throughout this trial.
“I’m just shocked,” an agitated Kamara told the president of the court Thierry Fusina. “I don’t know him. These people, it’s my first time to see them in my life. I don’t know them! They are lying on me. I’m not a criminal.”
Earlier in the day another witness to the alleged murder of the sick woman accused of witchcraft gave evidence that appeared to contradict testimony that he gave to an earlier investigating judge in the case.