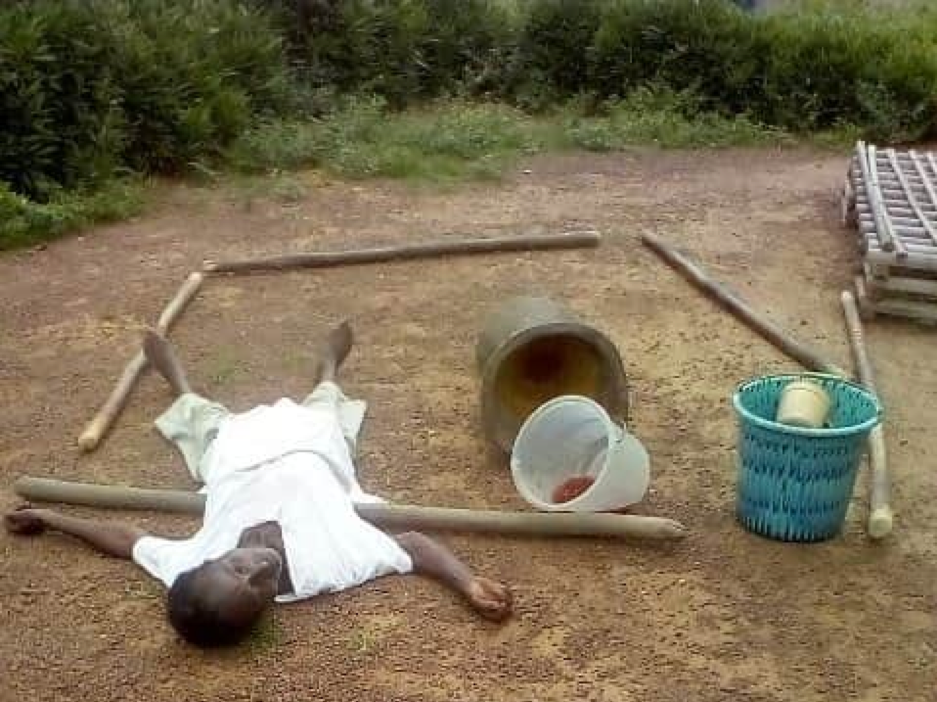
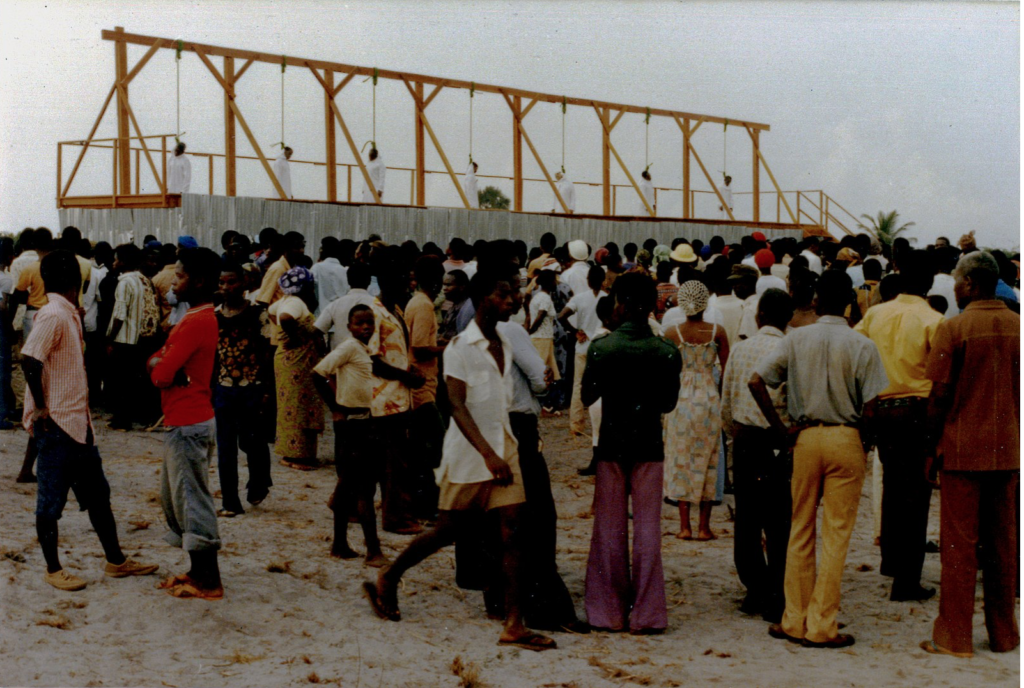
I recently posted an article on trial by ordeal in Liberia (‘sassywood trial’) which had cost six innocent people their lives, see my July 25 post Trial by ordeal reportedly kills six in Nimba County, Liberia.
In an apparent move to abolish or at least to restrict these traditional ways of administering justice the government has tried to restrict the powers of traditional chiefs by reducing the powers of traditional chiefs in a revised Local Government Act.
Such changes are not welcomed by the traditional chiefs as the following articles describes very well. Between the lines one can read that trial by ordeal is common in Liberia, a conclusion which hardly surprises. After all, the power of the central government is concentrated in the capital Monrovia and – maybe – also in the county capitals, but deep in the interior of Africa’s oldest independent state traditional chiefs rule. This explains their resistance.
Chiefs Vexed with Ban on Trials by Ordeal
Ministry of Internal Affairs cites “lack of evidence” in witchcraft cases

Published: August 9, 2024
By: Daily Observer, Liberia
If you thought the idea of “witch-hunting” in Liberia was just a metaphor to describe the ruling party’s alleged attempts to clamp down on and frustrate opposition elements, think again. Now, those who are actually in the business of determining who the actual witches are, have been ordered to stop.
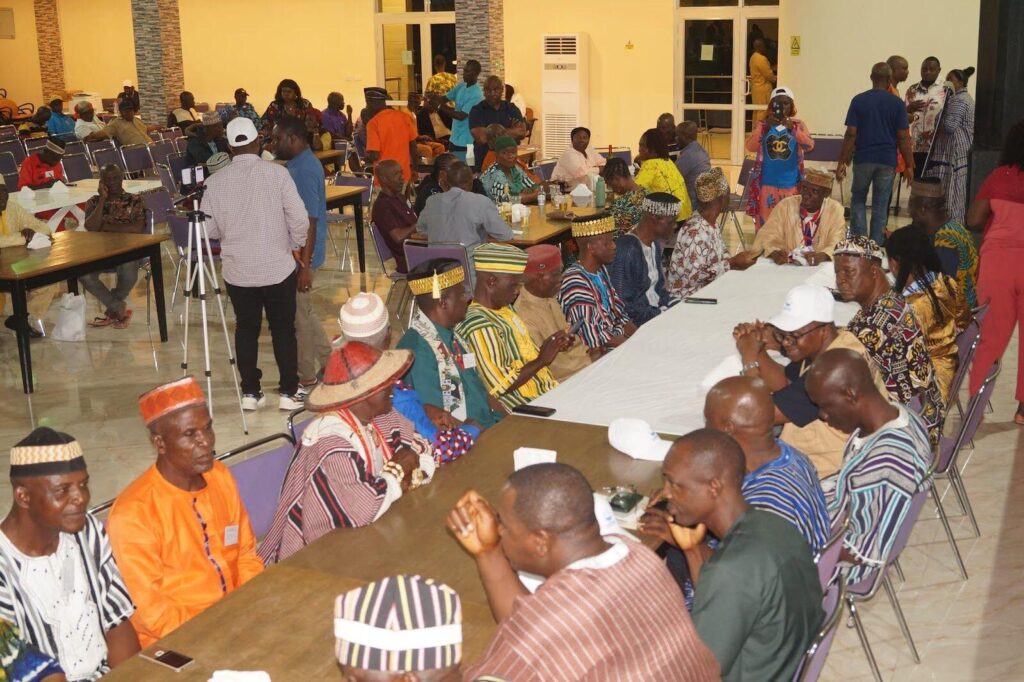
Scores of traditional chiefs and elders attending the Ministry of Internal Affairs National Orientation Workshop are disenchanted over the reduction of their powers in the revised Local Government Act. The chiefs expressed their disappointment over the situation as many of their traditional powers are now transferred to the county’s culture coordinator.
The new regulations restrict the chiefs from practices such as administering sassy wood or conducting trials by ordeal on persons accused of witchcraft.
During a presentation on the topic, Roles of County Council and the National Council of Chiefs, most of the responsibilities of the chiefs were scrapped, as the presenters ordered the chiefs to “stop giving sassy wood or trial by ordeal to anyone accused of being involved in witchcraft activities.
“All Zoe activities and traditional issues will strictly be handled or monitored by the culture coordinator and then make a report to the County Superintendent,” said Assistant Minister Emmanuel Wheinyue, one of the presenters.
The chiefs voiced their frustration at the workshop, highlighting that their roles have been significantly diminished by the recent legislative changes.
Chief James Peh Ssyan of River Gee County explained that since 1847, the roles of chiefs in the country have been immersed, in terms of settling disputes in their respective chiefdoms. Now, he said, the new law is mainly designed to scrap the chiefs of their powers.
“Why do you, the book people, want to trick us, when we were elected by the elders and we used to preside over cases surrounding zoes, witchcraft activity and now you are coming to say we cannot handle matters,” Chief Ssyan asked.
Paramount Chief Domah of Nimba County asked for a description of their (chiefs’) new responsibilities, where witchcraft cases surrounding his district are concerned. The response from the presenter was that, since there is no evidence in witchcraft cases, someone who feels bewitched should go to court with his or her evidence.
Additionally, the revised Local Government Act requires chiefs to report to the district commissioner monthly, emphasizing advisory roles for paramount chiefs instead of adjudicating cases.
Even though the roles and responsibilities of the Chiefs are not spelled out, the Ministry of Internal Affairs asked all chiefs to write a report to the district commissioner every month.
The elimination of traditional practices like sassy wood rituals has sparked concerns among some attendees, who fear an increase in witchcraft activities with the abolition of customary methods.
The workshop concluded with the election of various council officials and preparations for the upcoming election of the National Council of Chiefs.
Meanwhile, day four of the conference climaxed with the election of the superintendent council and city mayor council, respectively.
The superintendents elected Nimba County Supt. Kou Meapeh Gono as Chairperson of the Supt. Council with a three-year term, while Gbarnga City Mayor was elected Chairperson of the Mayors’ Council for a term of two years.
Mr. John Alexander Nyahn Jr. was also elected as head of the County Council Union.
Internal Affairs Minister Francis Nyumalin had a series of banquets, first for the 15 city mayors representing their counties’ capitals and on Wednesday, he prepared another banquet for 45 chiefs who had come to Ganta to participate in the event.
Meanwhile, the election for officials of the National Council of Chiefs is expected to be held on Friday, August 9, 2024.
The event gathered over 350 participants, including government officials and chiefs from across the country. These include 15 superintendents, 15 county administrative officers, 15 development officers, 15 fiscal affairs officers, 15 county council heads, all the 15 service centers’ heads, 45 chiefs, and top-level officials of the Internal Affairs Ministry, among others.
Source: Chiefs Vexed with Ban on Trials by Ordeal